What a beautiful weekend I enjoyed recently. Not only was it Mother’s Day and I had my first-born, ‘two-days-before-Mother’s Day’ son nearby, but we enjoyed a walk up the dirt road behind neighbouring cottages on Lake Muskoka near Torrance, a few hours north of Toronto, and found a treasure trove of native spring wildflowers on both the lake side and the crown land side. The photo below is of the road from another May. This year, the sustained, cool weather meant leaves were just breaking on the trees and best of all the blackflies had not yet emerged!
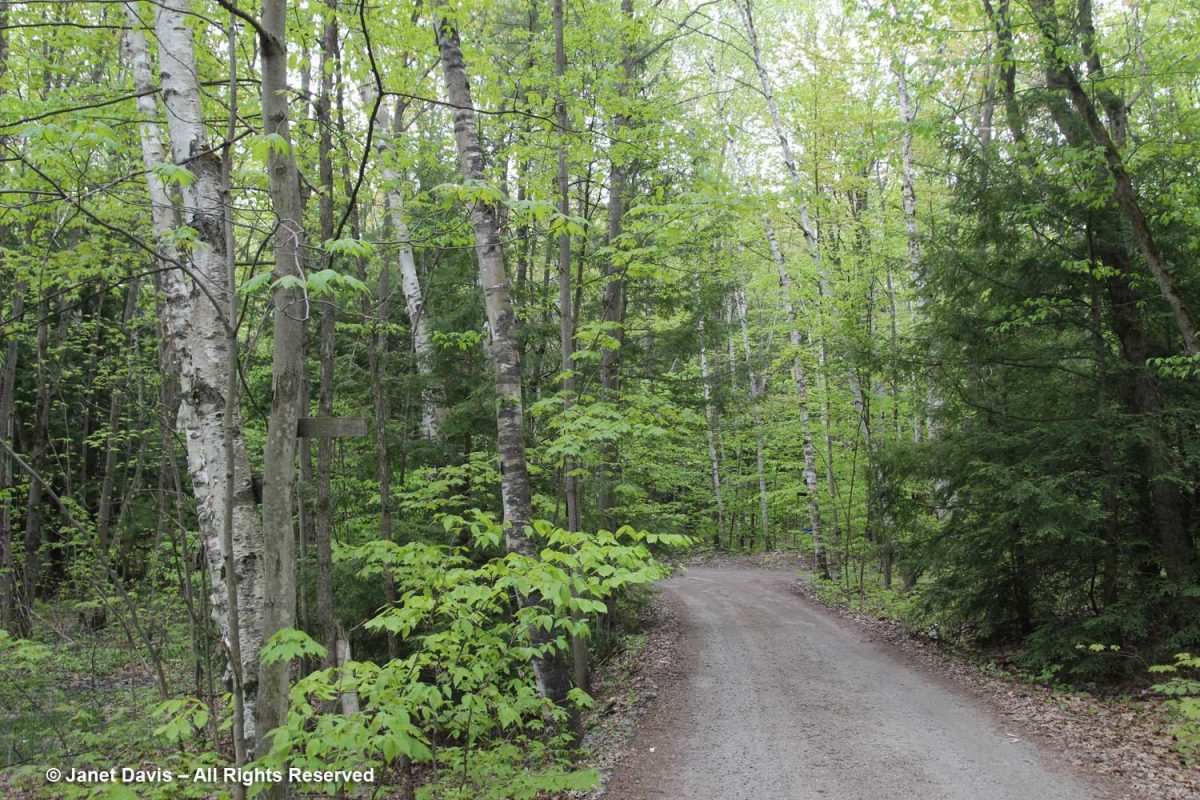

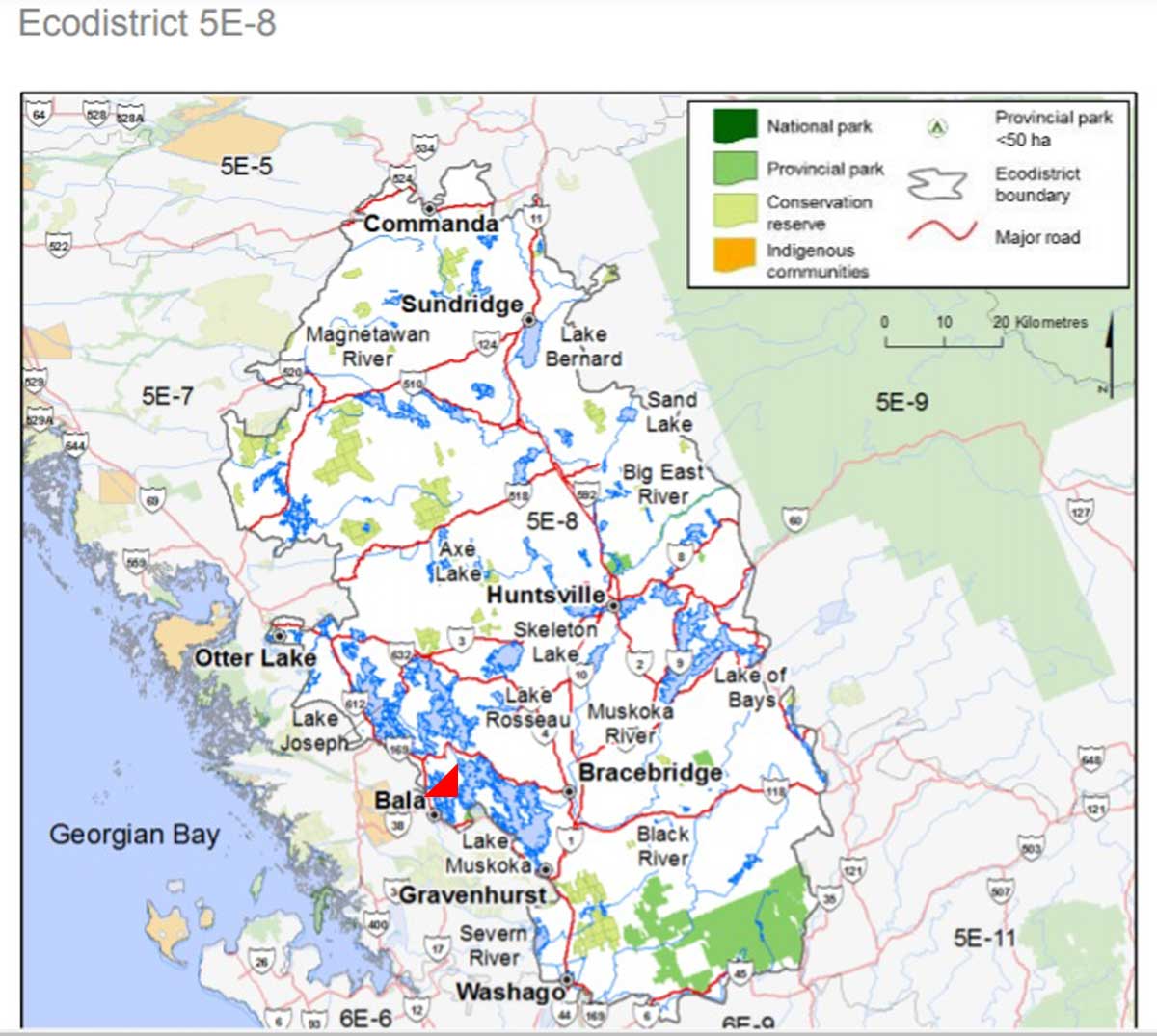
Ecologically, the address of the dirt road near Bala marked with the red arrow, below, is (broadest to narrowest classification) Ontario Shield Ecozone, Georgian Bay Ecoregion 5E, Huntsville Ecodistrict 5E8. According to the provincial classification: “The Huntsville Ecodistrict is an undulating to rolling landscape underlain by Precambrian bedrock. The terrain, particularly in the west, has been heavily influenced by glacial Lake Algonquin that inundated the area about 11,000 years ago. As the land emerged from underneath the ice, morainal material was deposited. The area was then submerged under the glacial lake, which removed or reworked much of the material through wave action and fluctuating lake levels. The western portion of the ecodistrict is characterized by a mosaic of bedrock ridges with a discontinuous, shallow layer of morainal material, bare bedrock, and pockets of deeper glaciolacustrine sediment.” Most of our district is covered by deciduous and mixed forest, including northern red oak, red maple (sugar maples predominate in the east part of the ecodistrict), yellow birch, paper birch, American beech, basswood, eastern hophornbeam, eastern hemlock and eastern white pine.
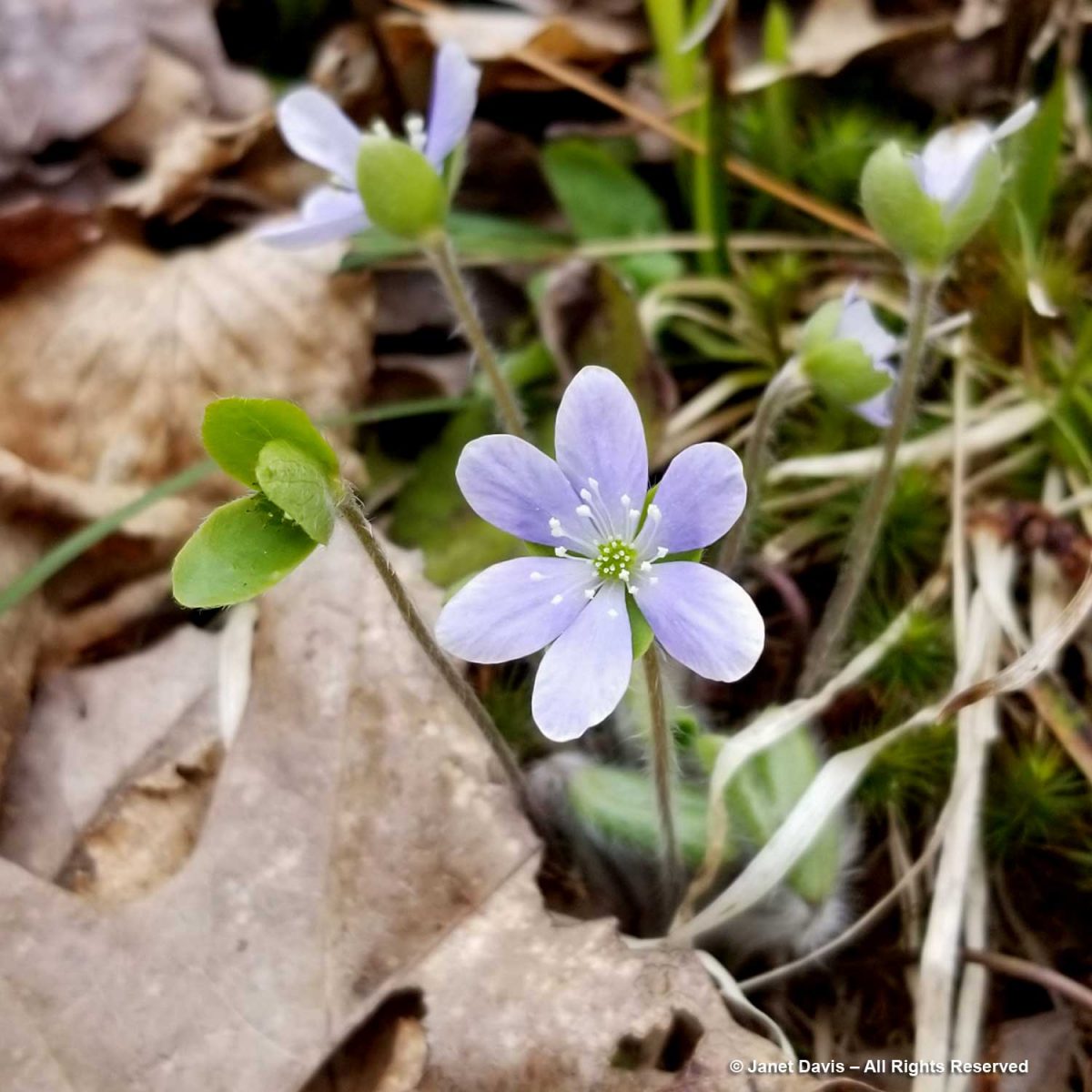
Though we’ve had our cottage for two decades, it was precisely the right moment to enjoy a bounty of spring wildflowers I’d never seen flowering all together, most of them dependent on the dappled light under deciduous trees before the leaves emerge to cast heavier shade. Plants like round-lobed hepatica, Anemone americana, both the white and purple forms.
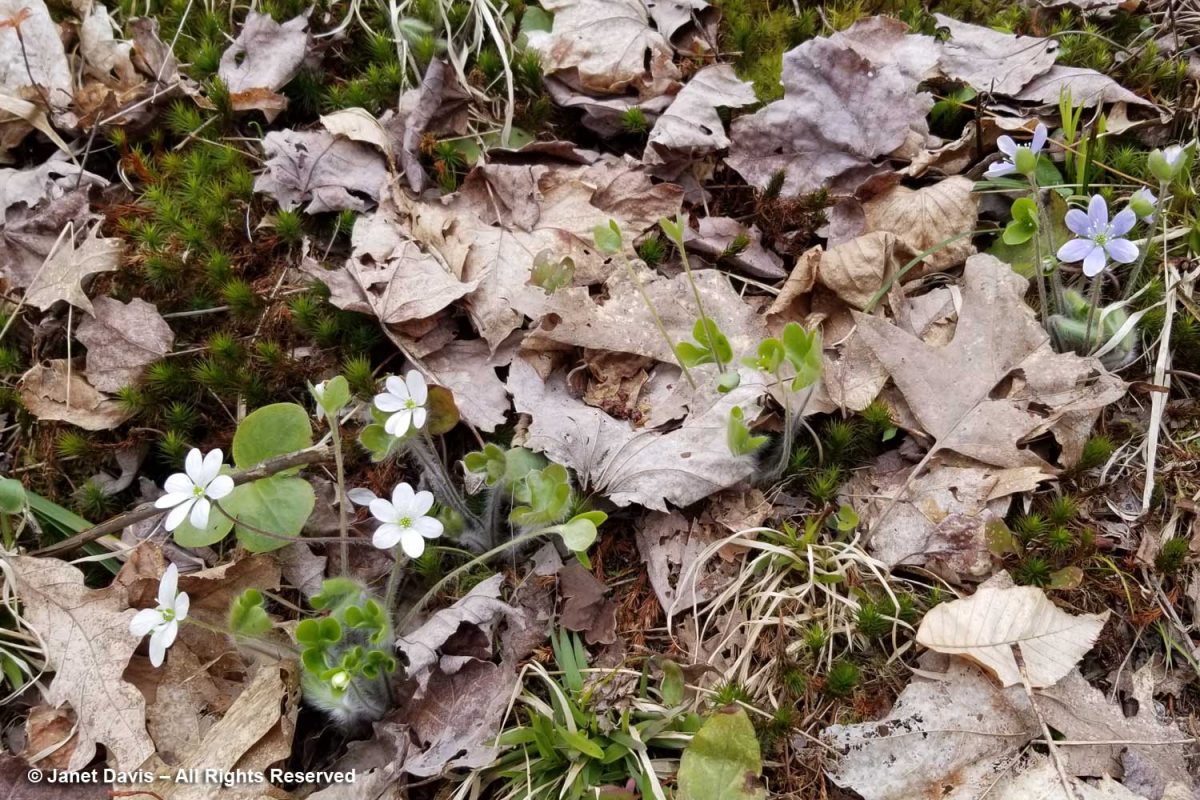

Many gardeners think they need to do a clean-up in autumn or spring, removing every leaf to expose bare soil; indeed, I heard a leaf-blower droning away on a cottage property nearby. But nature is under no such misapprehension; the spring understory here on Lake Muskoka is thick with successive years of red oak and beech leaves, all contributing to the health of the soil and the richness of the forest. Hepatica has no trouble emerging through them, pushing fresh new leaves and fuzzy flower stems up through last year’s bronzed foliage which then withers away.
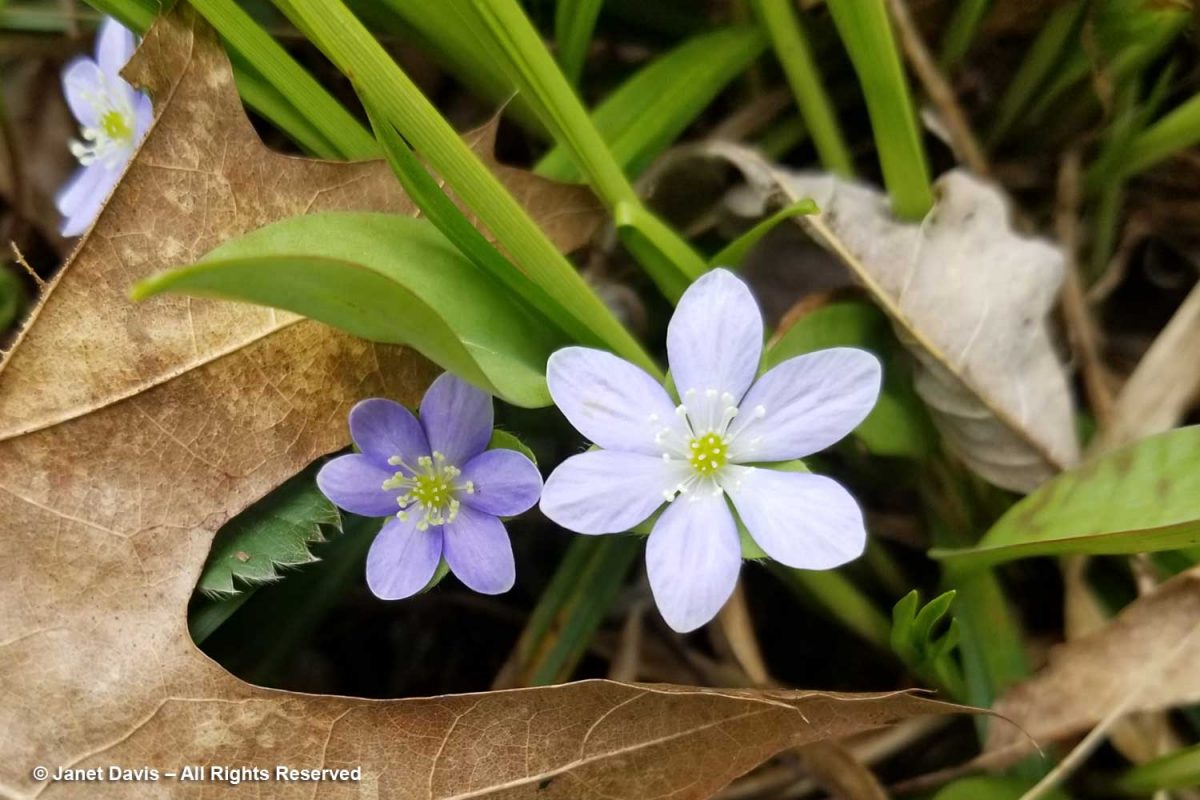

Like many plants, DNA sequencing has resulted in hepaticas undergoing a scientific name change. They’re now placed in the Anemone genus.

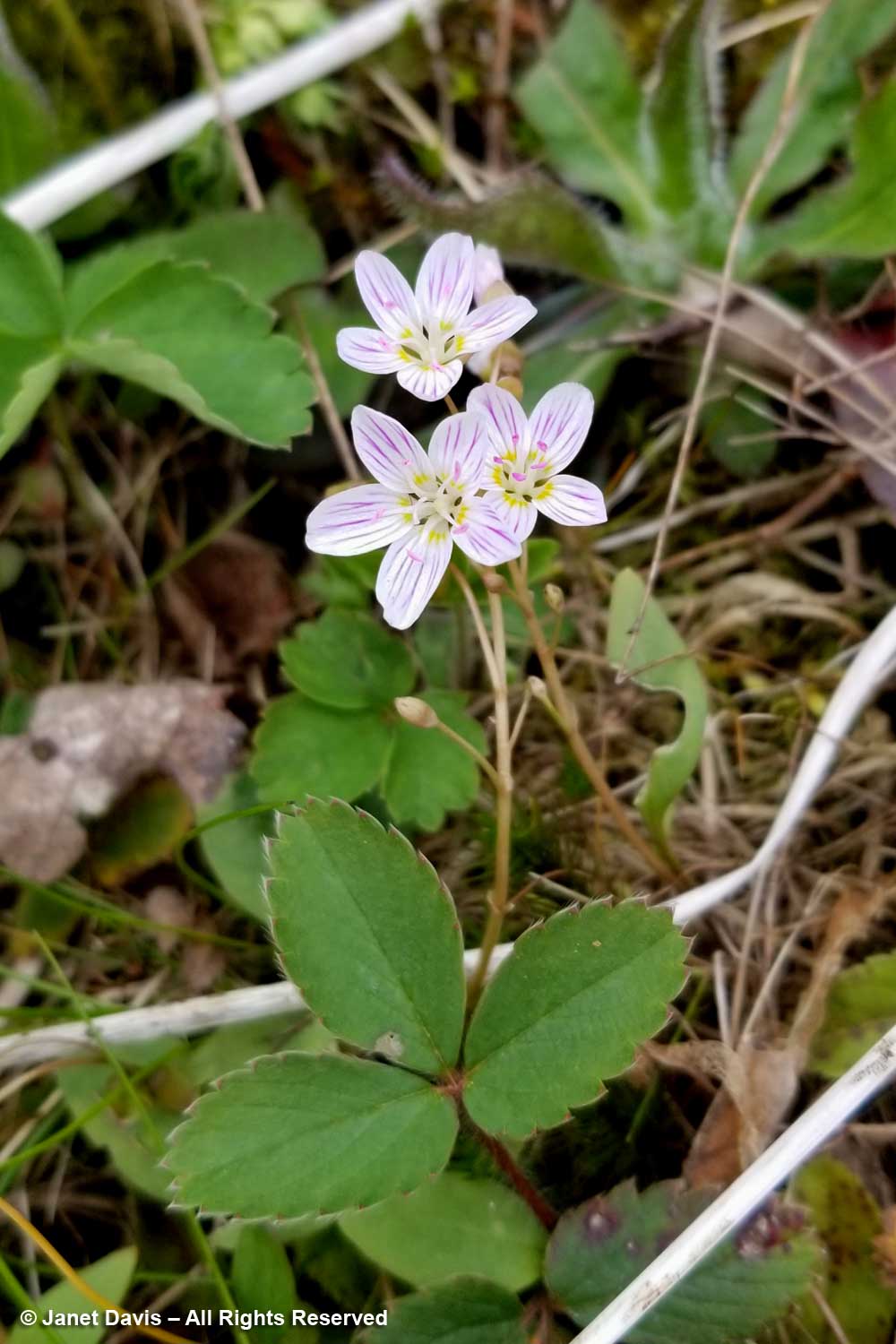
Carolina springbeauty (Claytonia caroliniana) was showing its mauve-striped face here and there too, the flowers so tiny they’re easy to overlook. It grows from a corm and is one of our spring ephemerals, plants that disappear and become dormant by summer.

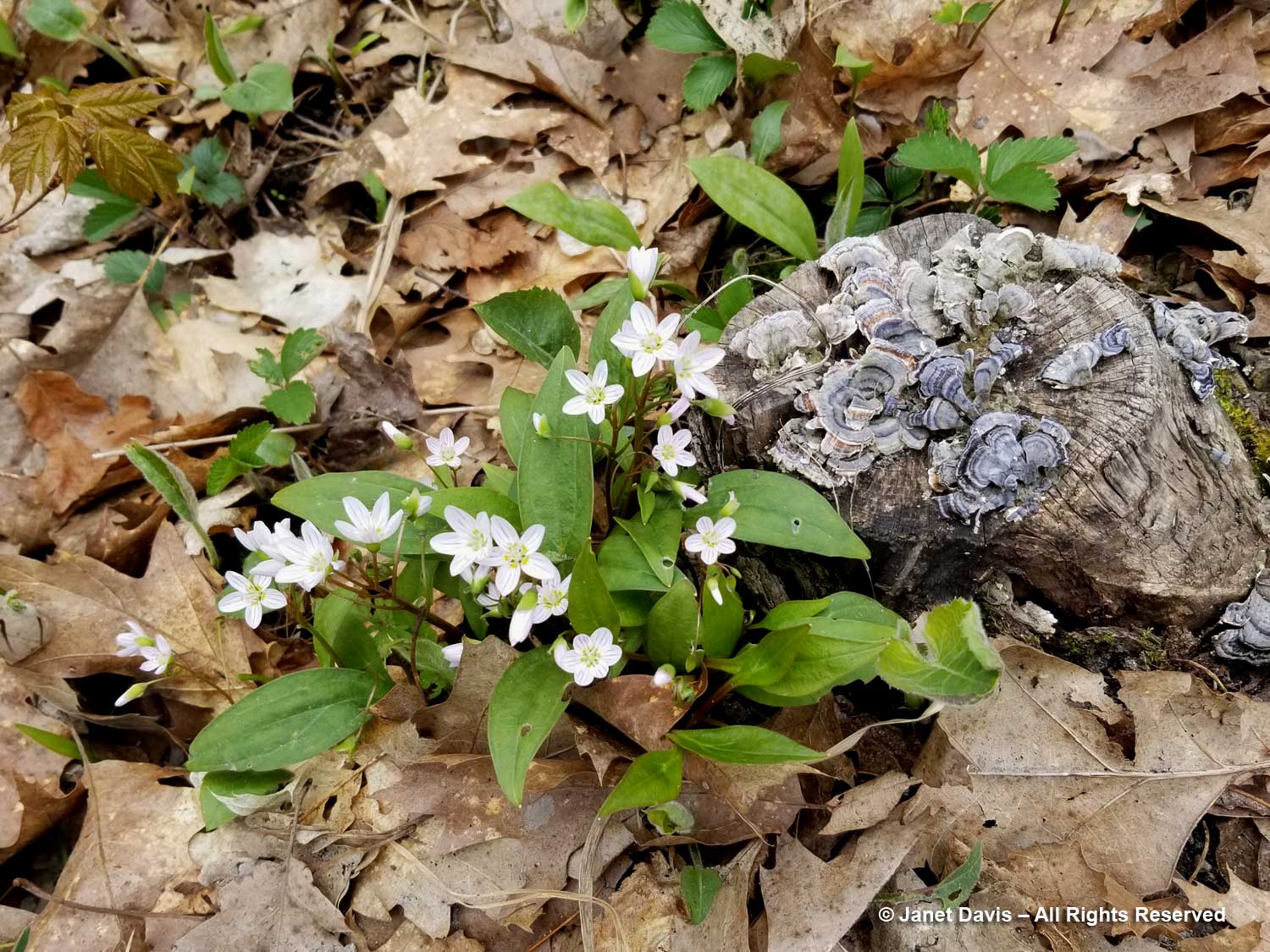
I was struck by the proximity of the spring beauty and the decomposing stump bedecked by turkey tail fungus (Trametes versicolor)…..

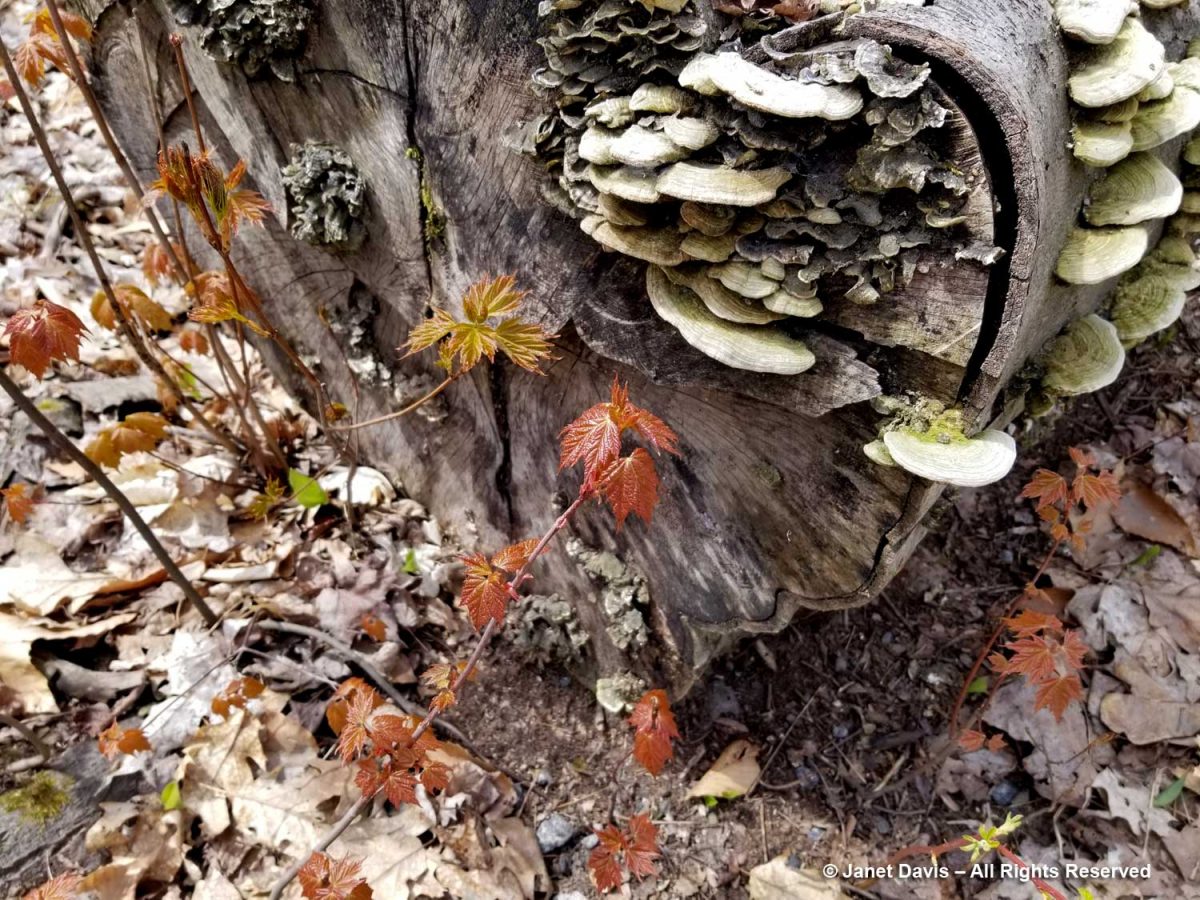
….and another fungi-rich stump flanked by masses of red maple seedlings (Acer rubrum). The coming and the going, the cycle of decomposition and renewal in this mixed forest.

Birches (Betula spp.) are not long-lived compared to other deciduous trees, usually around 50-70 years in our northern climate. Sometimes decomposition begins when they’re still standing, like this trunk with tinder fungus (Fomes fomentarius) all the way up. It’s called tinder fungus because it can be used to make a fire; in fact the Tyrolean Ice Man Ötzi, whose 5000-year-old corpse was revealed by melting glaciers near Bolzano, Italy in 1991, had a piece on a cord around his neck.
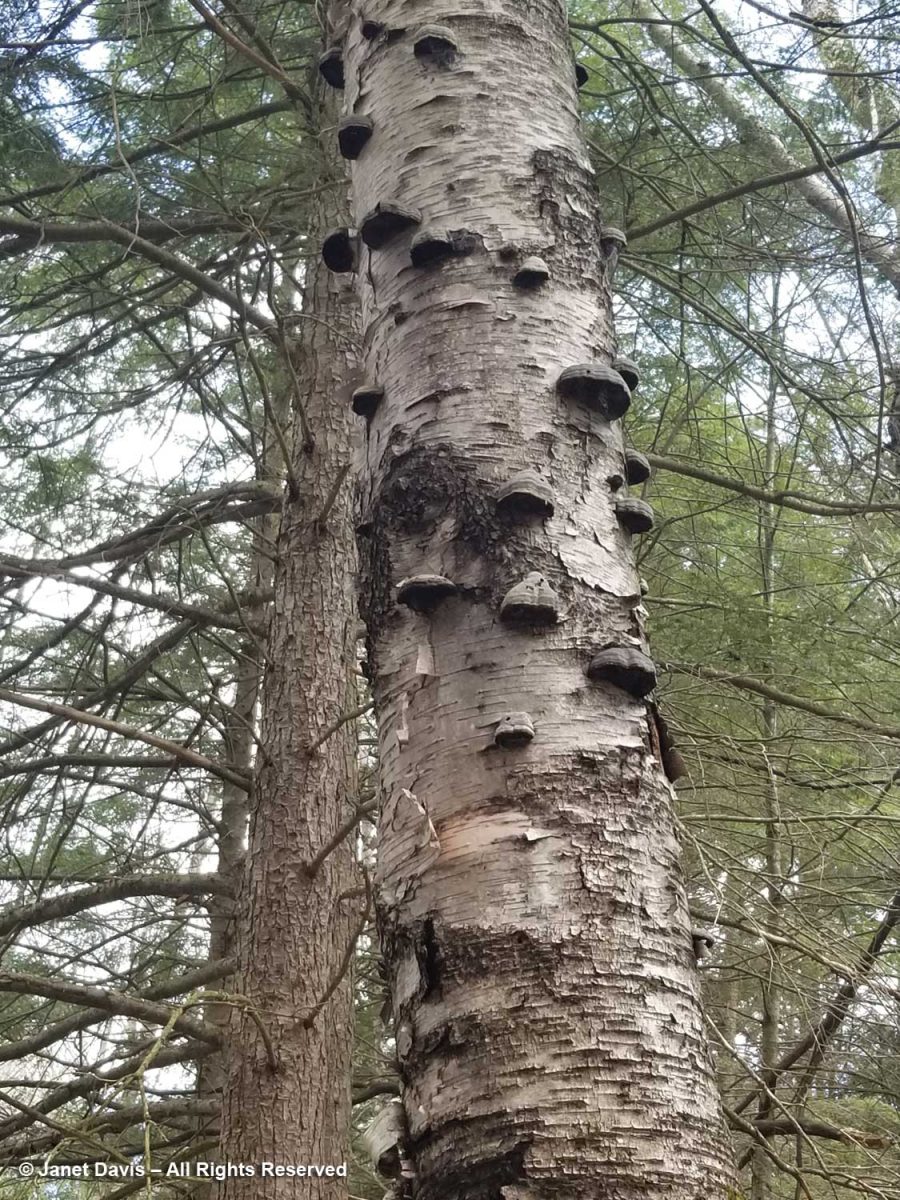

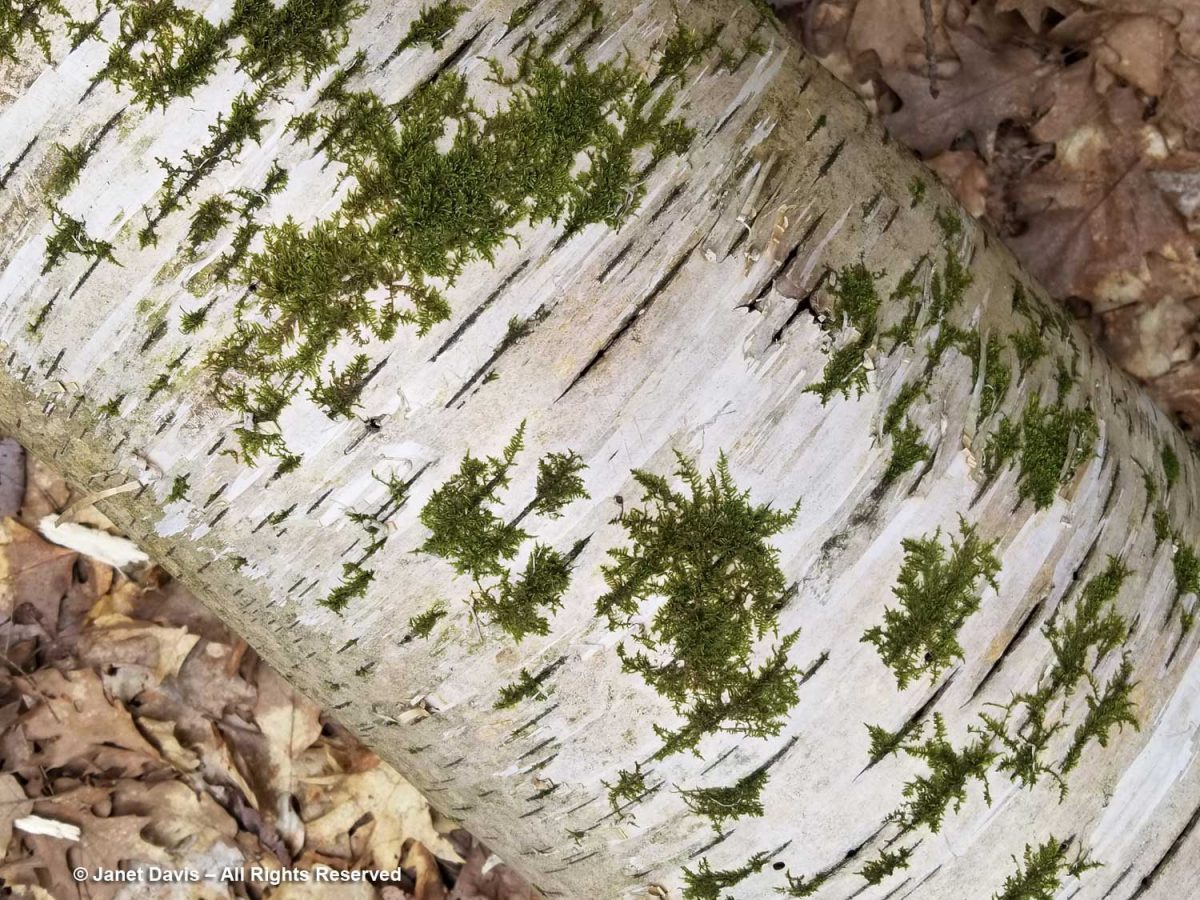
When birches fall, it takes little time before moss spores find them and begin to spread their green tentacles. Before long, the birch becomes part of the forest floor.

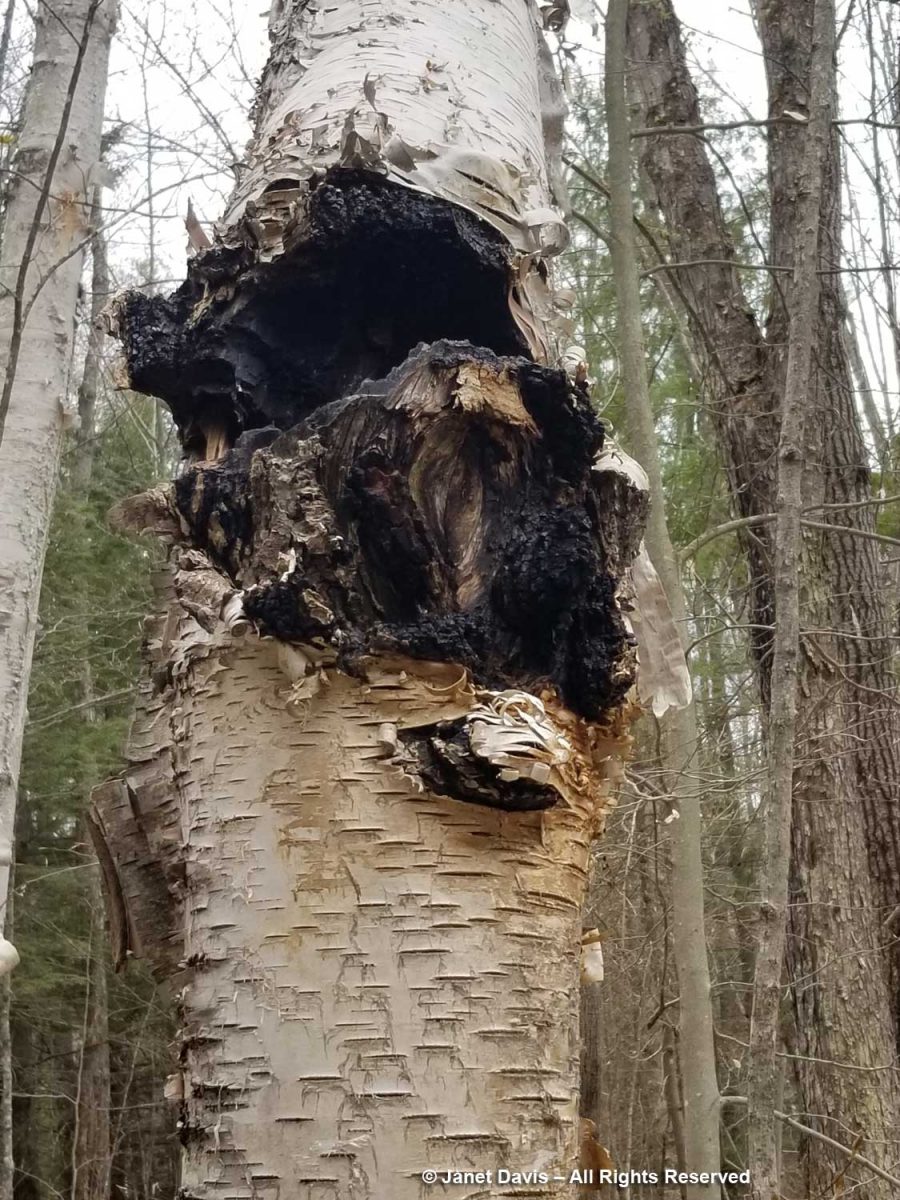
Though rare, a lightning strike can also kill a birch. This one would have made a loud crack in one of our summer thunderstorms.

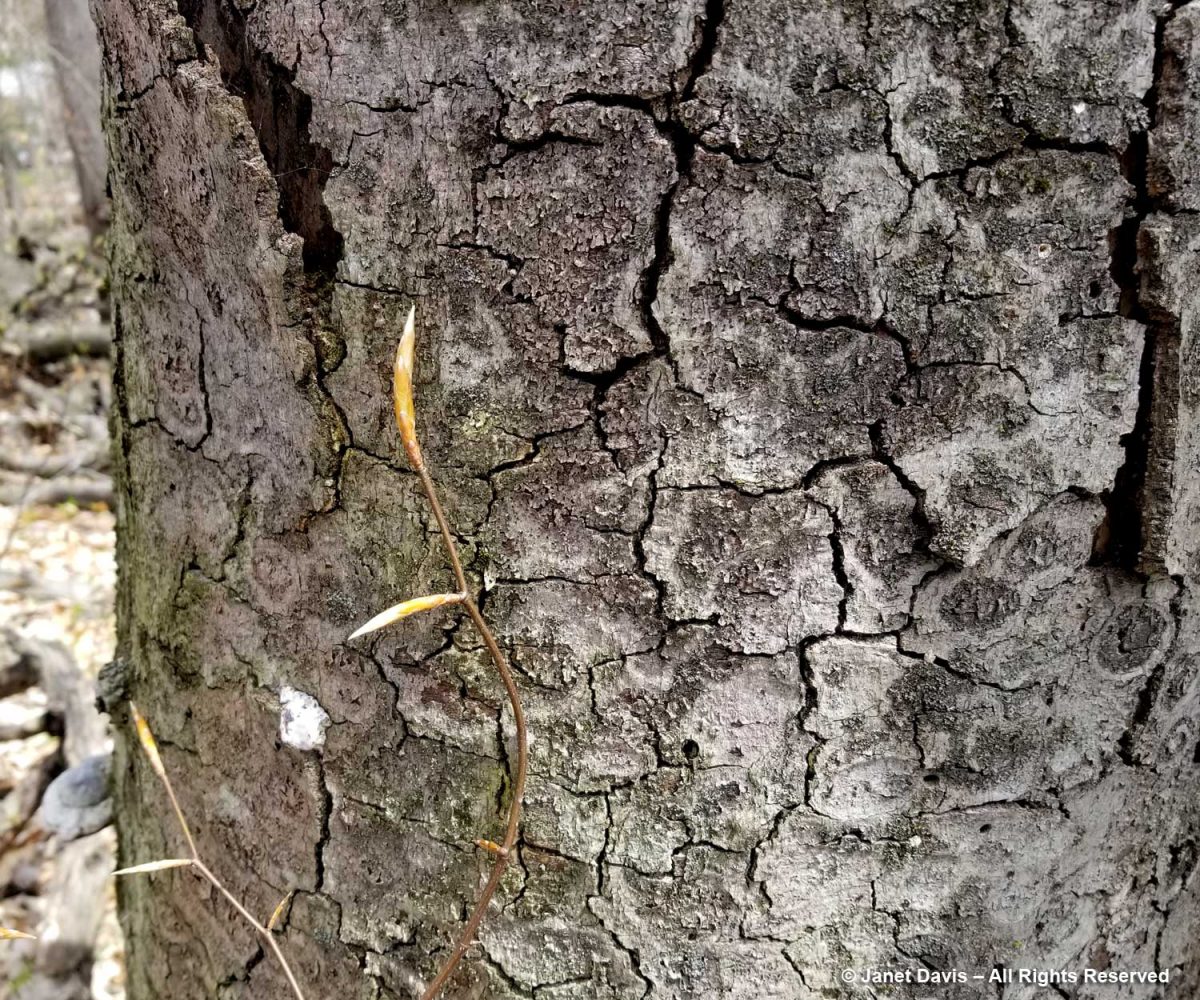
I found this juxtaposition poignant: a young American beech sapling (Fagus grandifolia) growing against the decaying trunk of a beech killed by beech-bark disease, a terrible insect-fungus plague taking a toll on our central Ontario forests, especially those where beeches grow with hemlocks. The vector is a beech-scale insect (Cryptococcus fagisuga) which, like many killers of our native species (e.g. Dutch elm disease) is an invasive from Europe. It admits a canker fungus called Neonectria faginata.

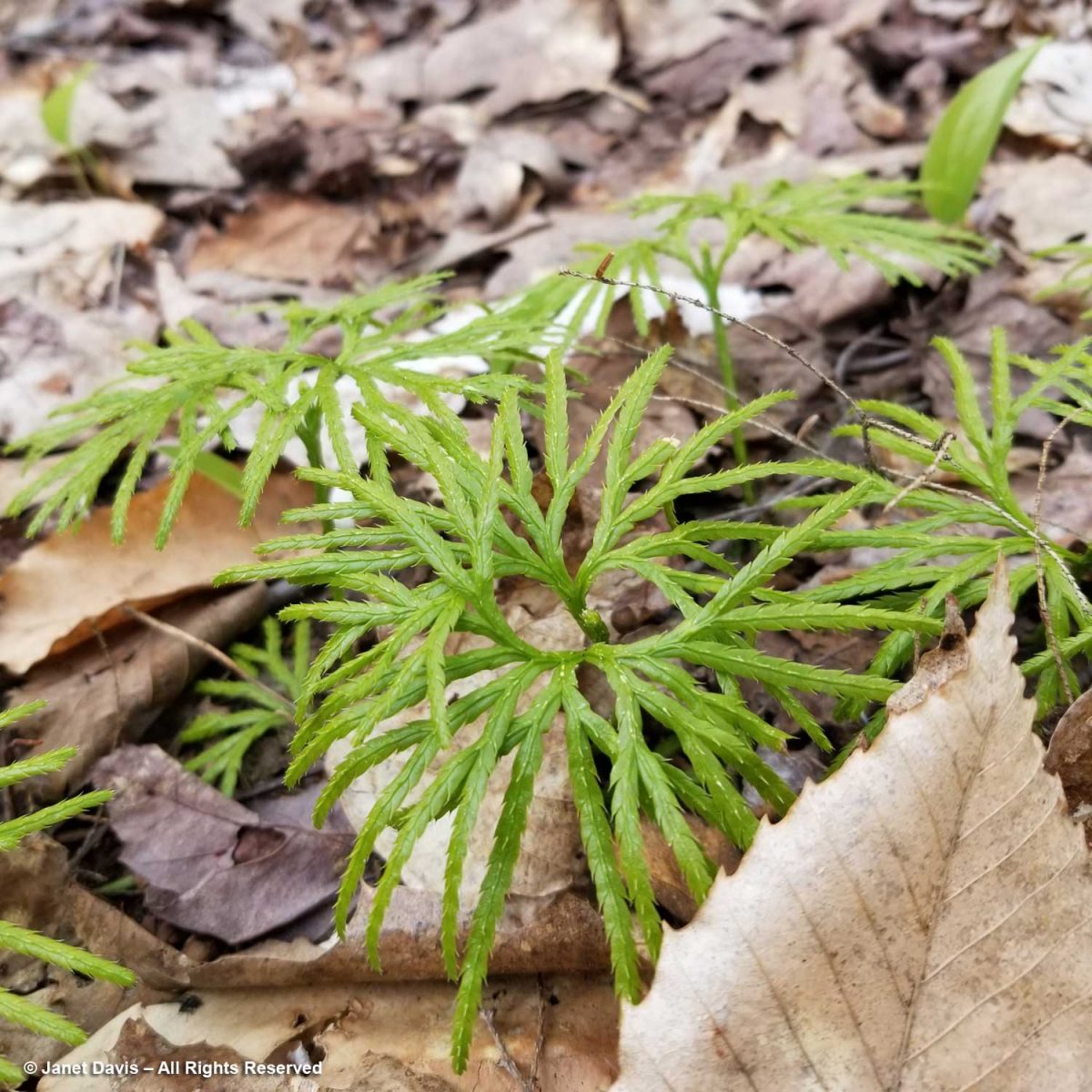
Groundcedar or fan club-moss, Diphastriastum digitatum is a lycopod, a throwback to the Carboniferous era (360-300 million years ago) when spore-forming plants like these formed forests of giant trees. Their decomposition and burial over millions of years gave the world its coal deposits.

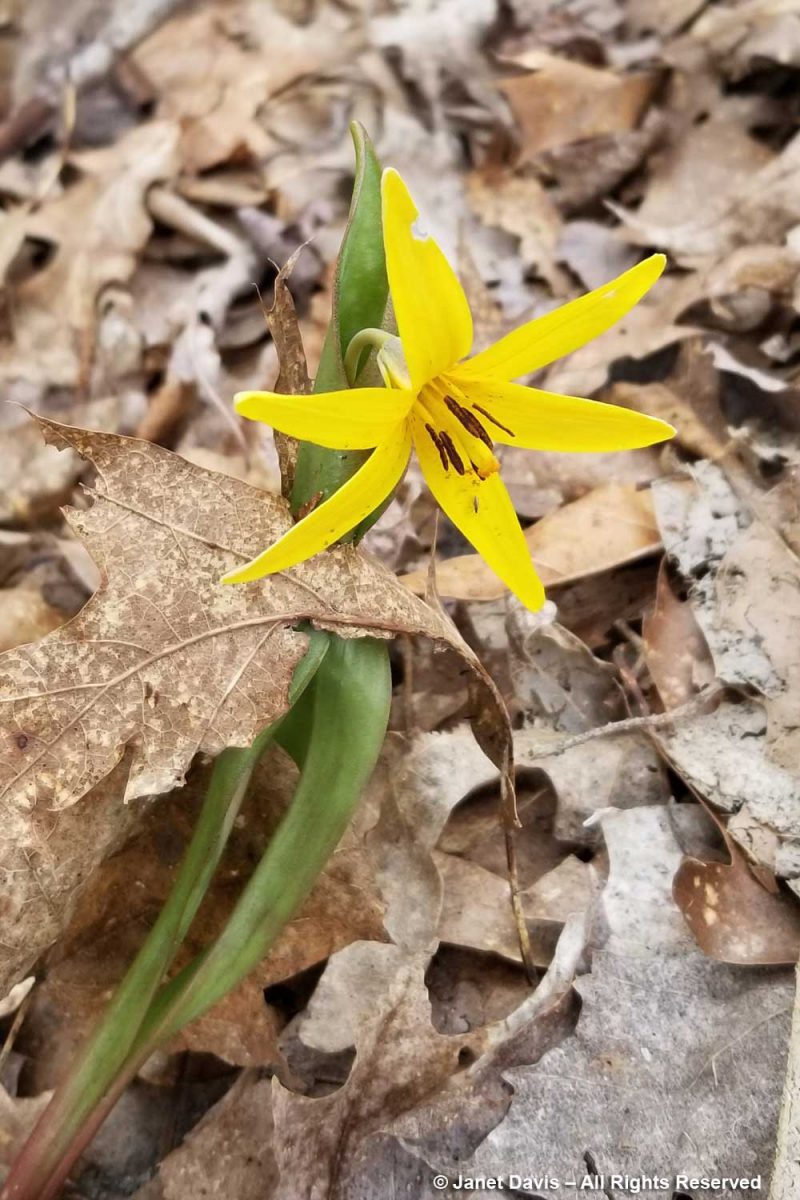
In low-lying areas, we found another spring ephemeral: dogtooth violet or trout lily Erythronium americanum which is not a violet but is a member of the lily family, Liliaceae. The “trout” part is because the mottled leaves resemble brook trout.

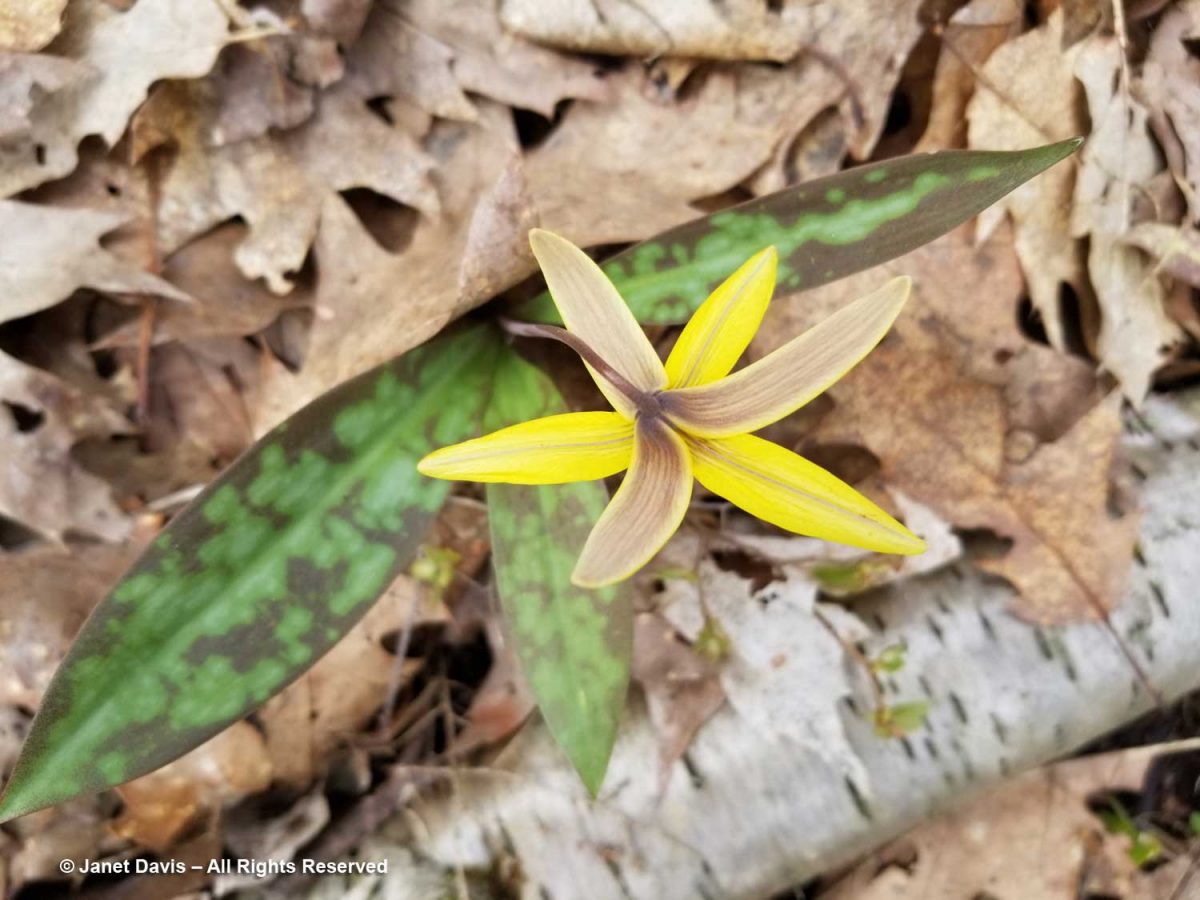
Although it looks like the flower has six yellow petals, in fact the reverse view shows the three brownish sepals.

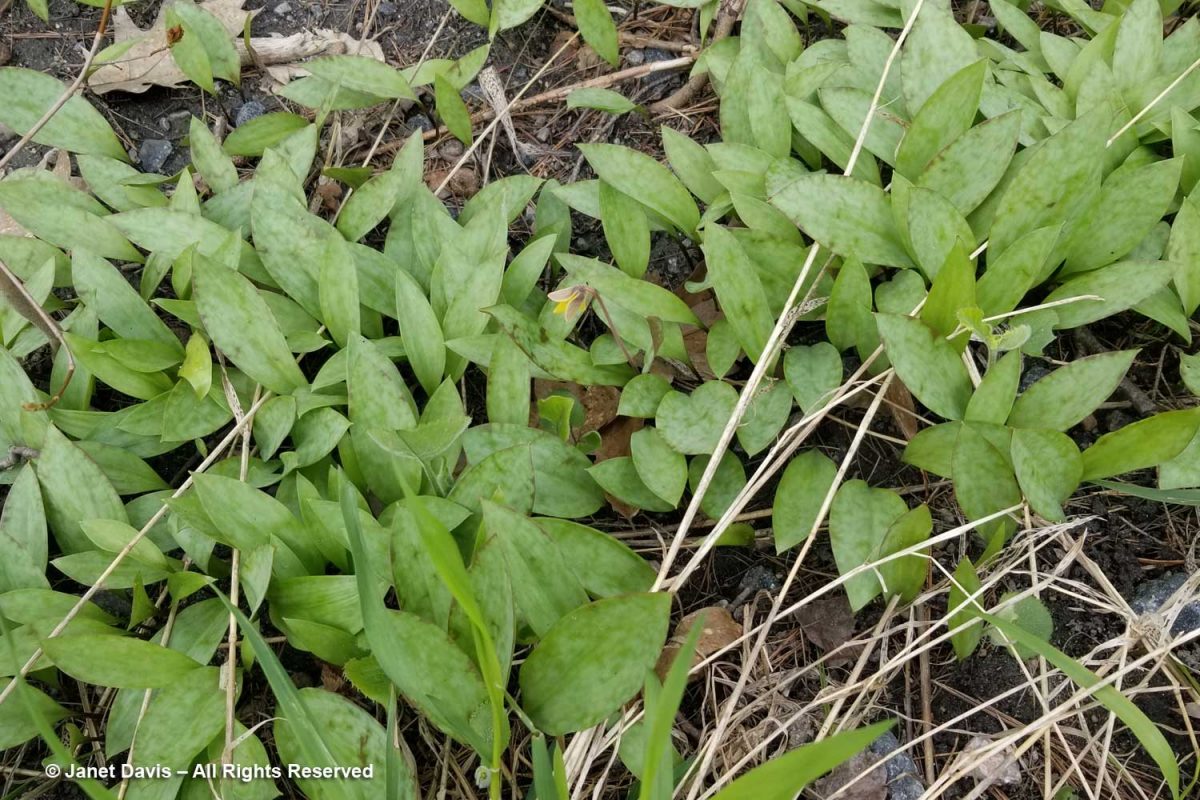
The ecology of dogtooth violet is fascinating. In some parts of these woods, it made up almost the entire ground layer, but only a few plants bore flowers, the rest just had leaves. In fact, Erythronium americanum takes 4-7 years to flower, and researchers have calculated that in any given population only 0.5% will bear flowers.

There’s a little wetland along the road that drains the forest from the west. It’s where spring peepers sing in April and mosquitoes gather when the weather warms.
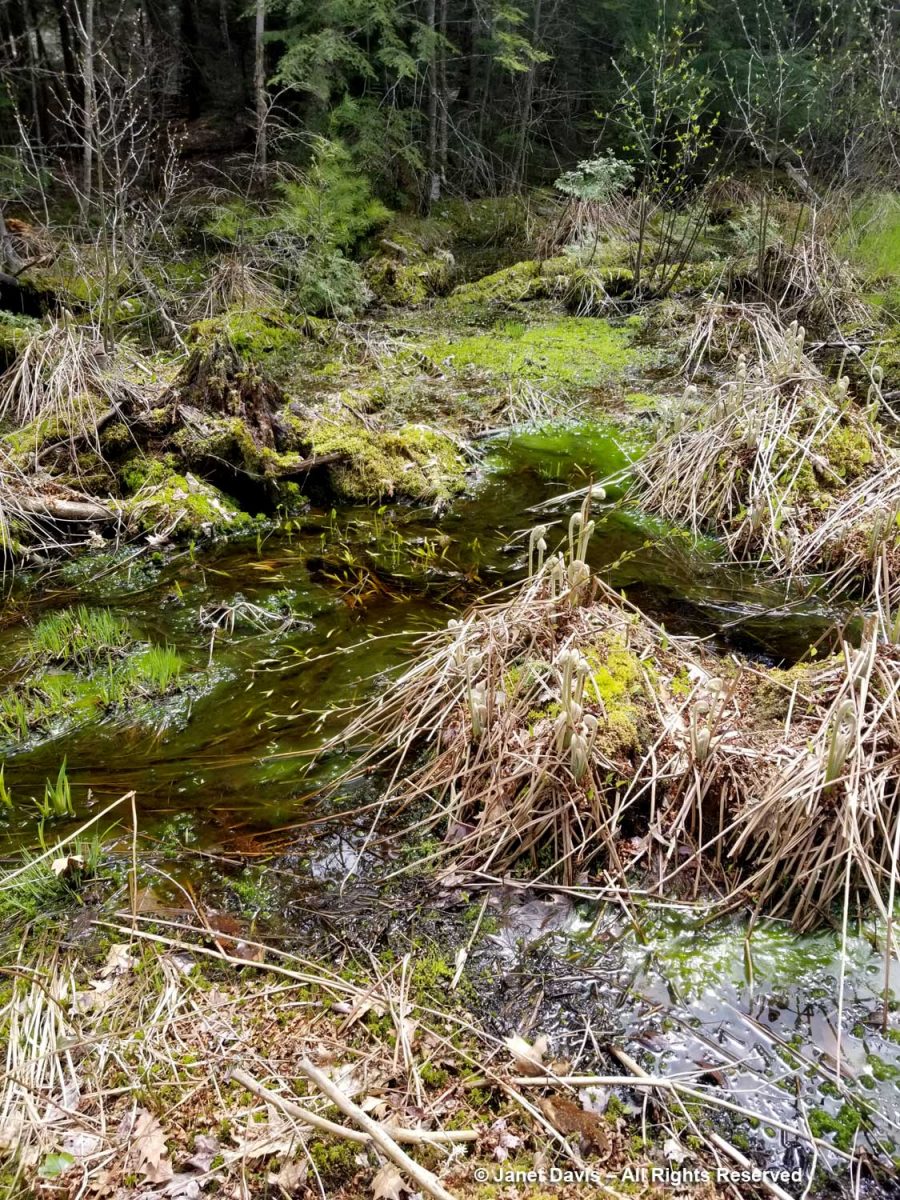

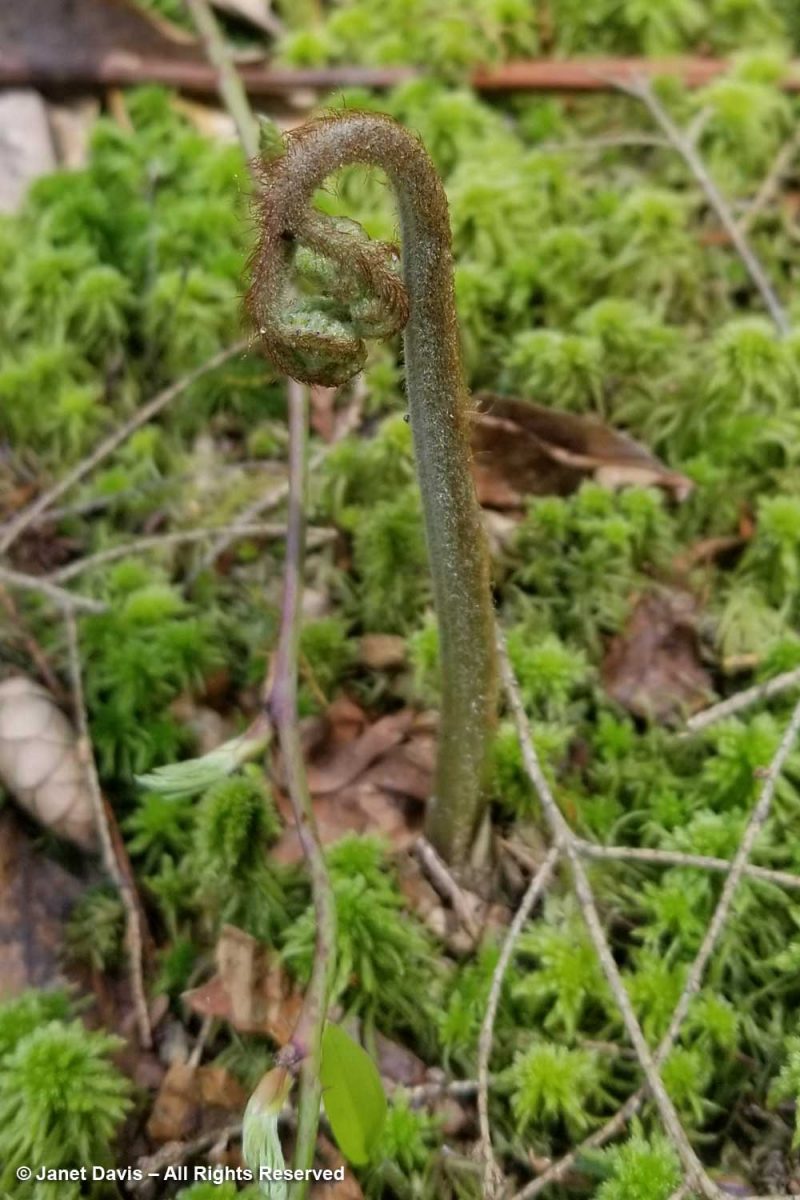
I went down onto the boggy mosses to get closer to the hummocks of cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum) which had just emerged….
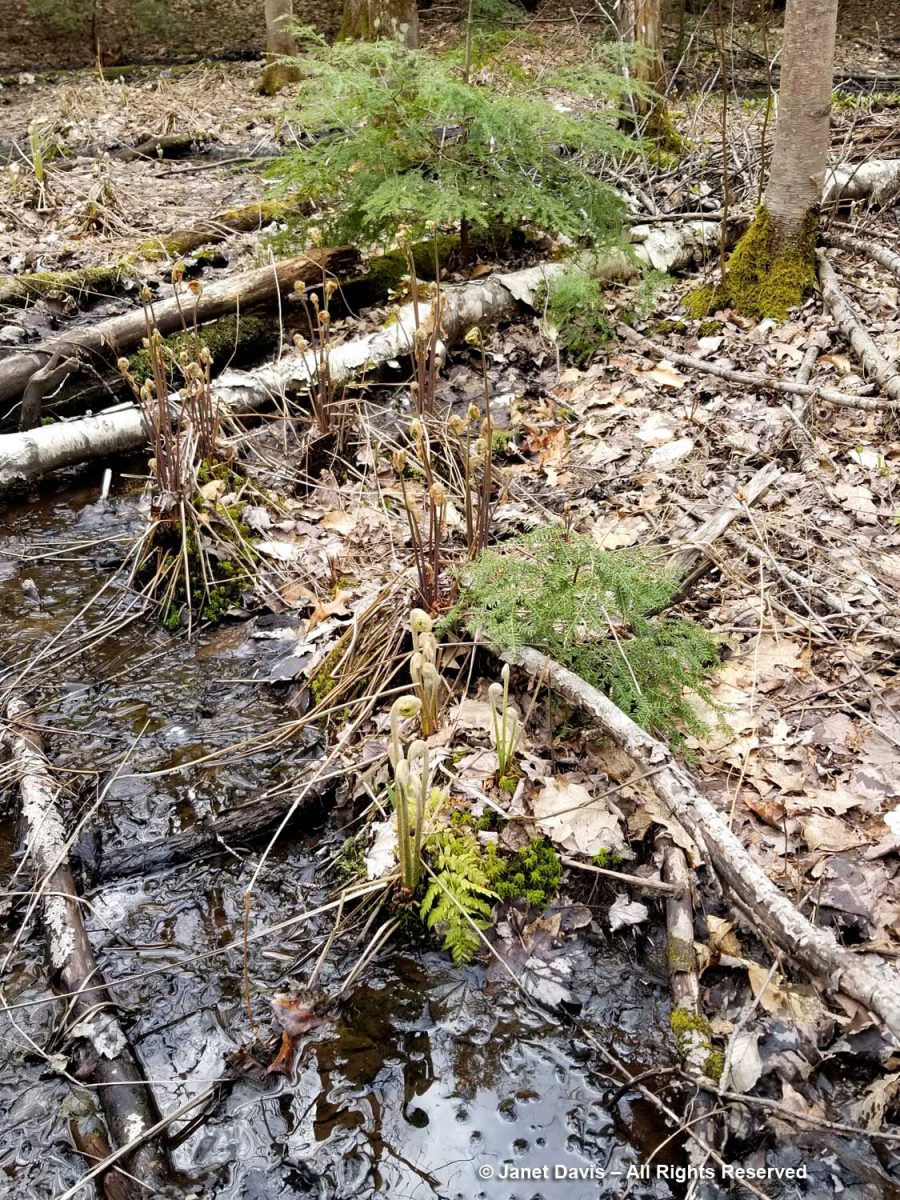

….. with their croziers wrapped in gauzy hairs. Cinnamon and royal fern (Osmunda regalis) are the principal wetland ferns here.
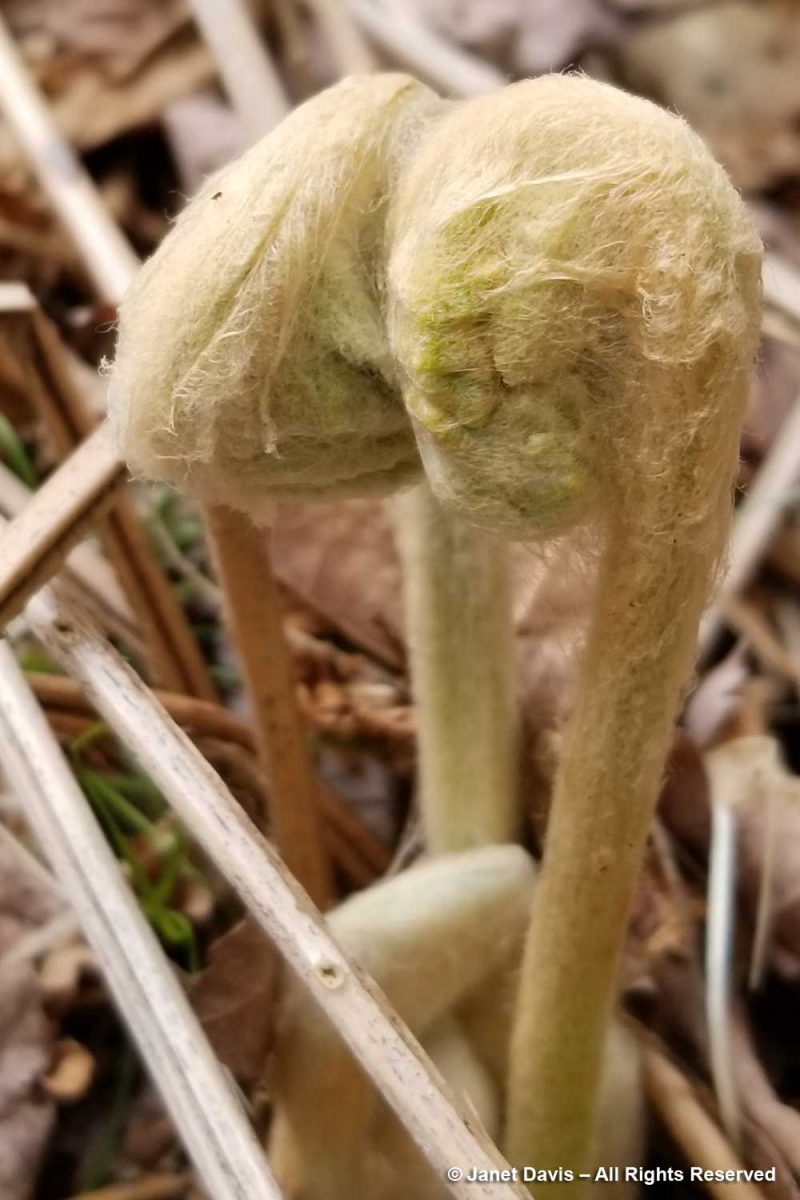

In springtime and after heavy summer rains, ground water moves through this wetland, passes under the dirt road in a culvert and wends its way as a creek through our friends’ property before splashing down into Lake Muskoka as a small waterfall. I made the video below to show it.
We found coltsfoot (Tussilago farfara) in flower at the edge of the road.
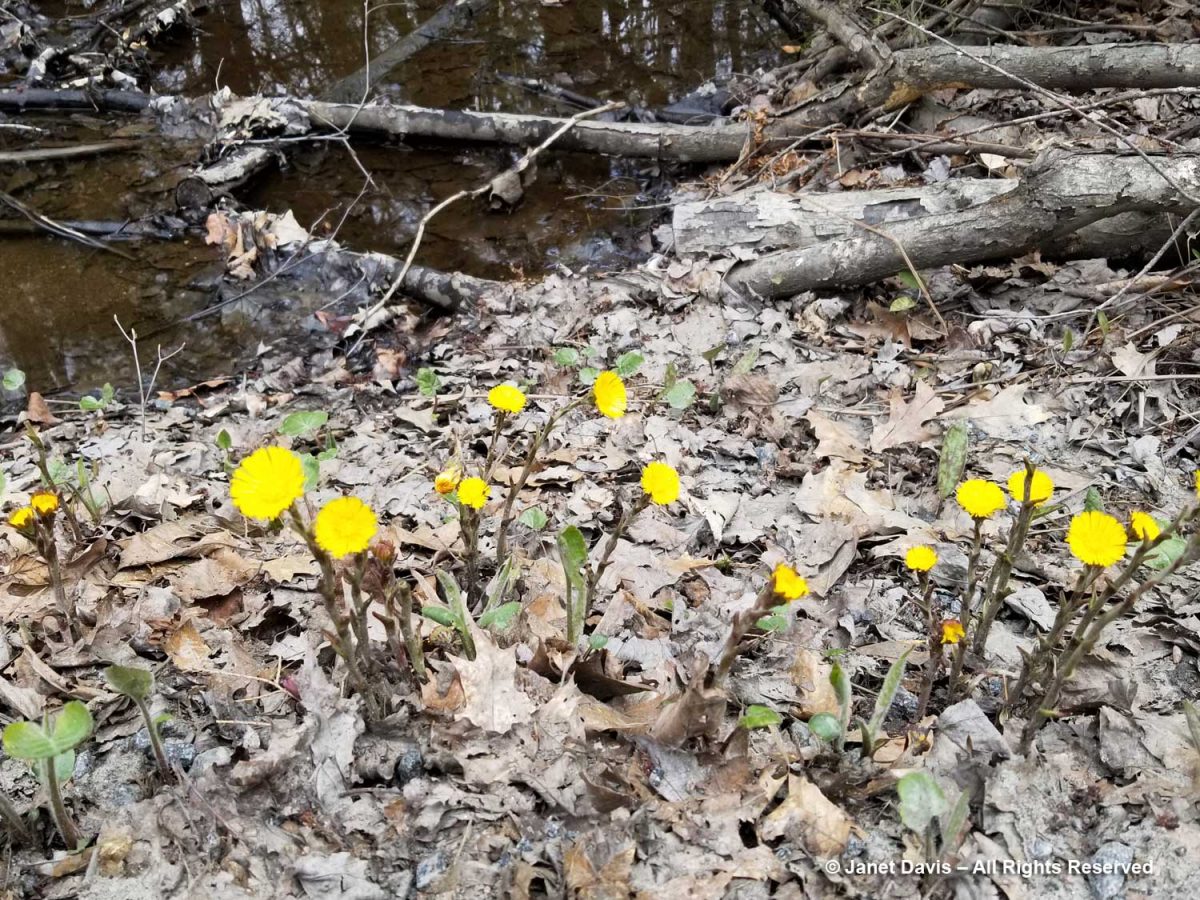

Native to Europe, Asia and North Africa, coltsfoot was used as a medicinal by early settlers – its name comes from the Latin “tussis” for cough and “ago”, meaning to act upon – and seed has made its way to throughout the region.

Ferns unfurled their croziers from the moss in the low spots.

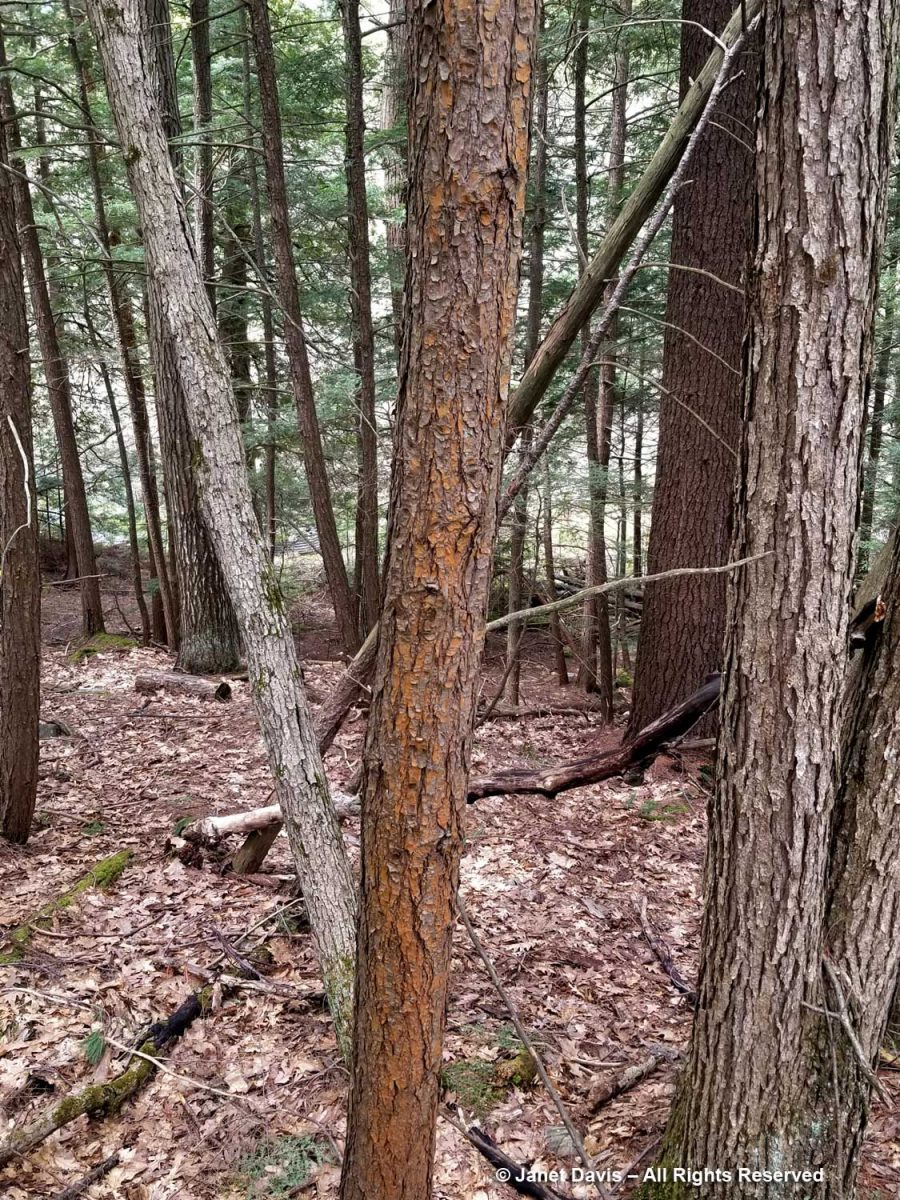
We noticed that several of the hemlocks and pines along the road had an orange-red flush to their bark, but only on the side exposed to the light. Some research revealed that this is a fairly recent condition called Red Bark Phenomenon or RBP, having been discovered and named about 10 years ago in New England. It is caused by a filamentous green algae (Chlorophyta) tentatively identified as Trentophilia whose cytoplasm contains an orange-red pigment.

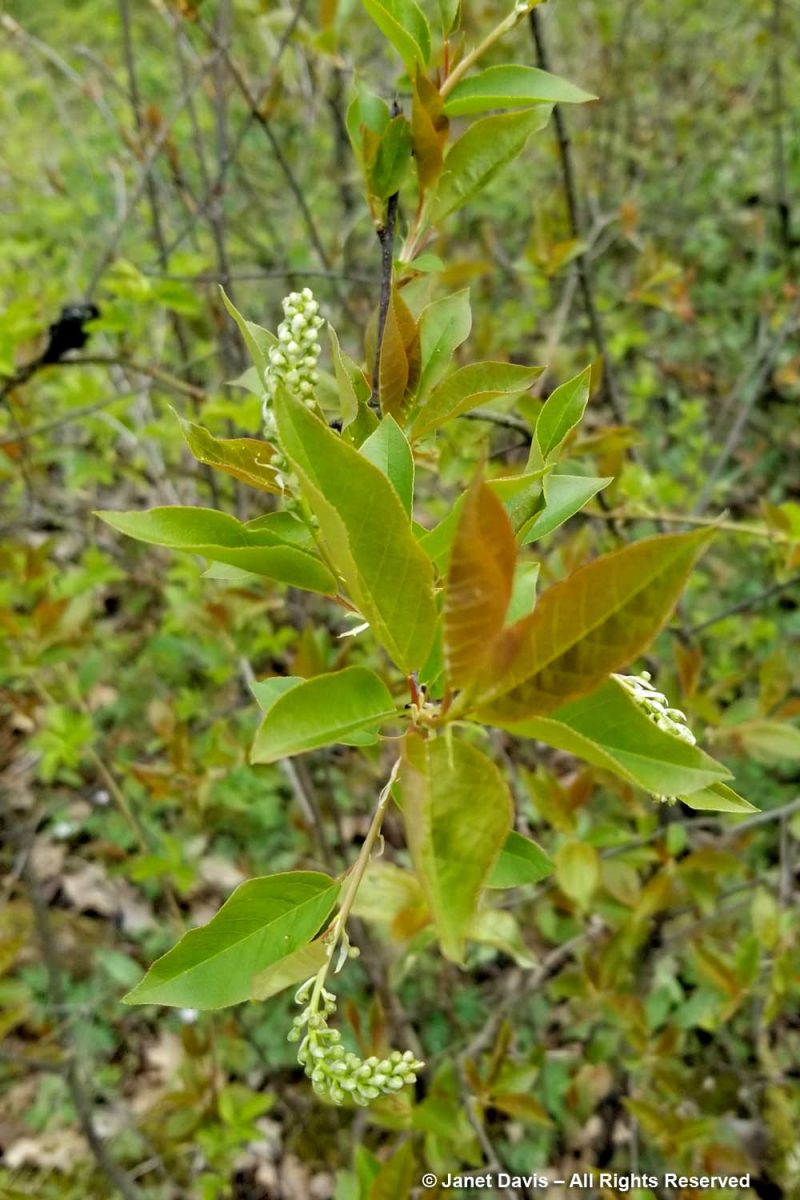
Patrick leaned into a little thicket of chokecherry (Prunus virginiana)….

….. not quite in flower. He detected a minty-basil fragrance, though the twigs are occasionally described as having an ‘almond’ aroma.

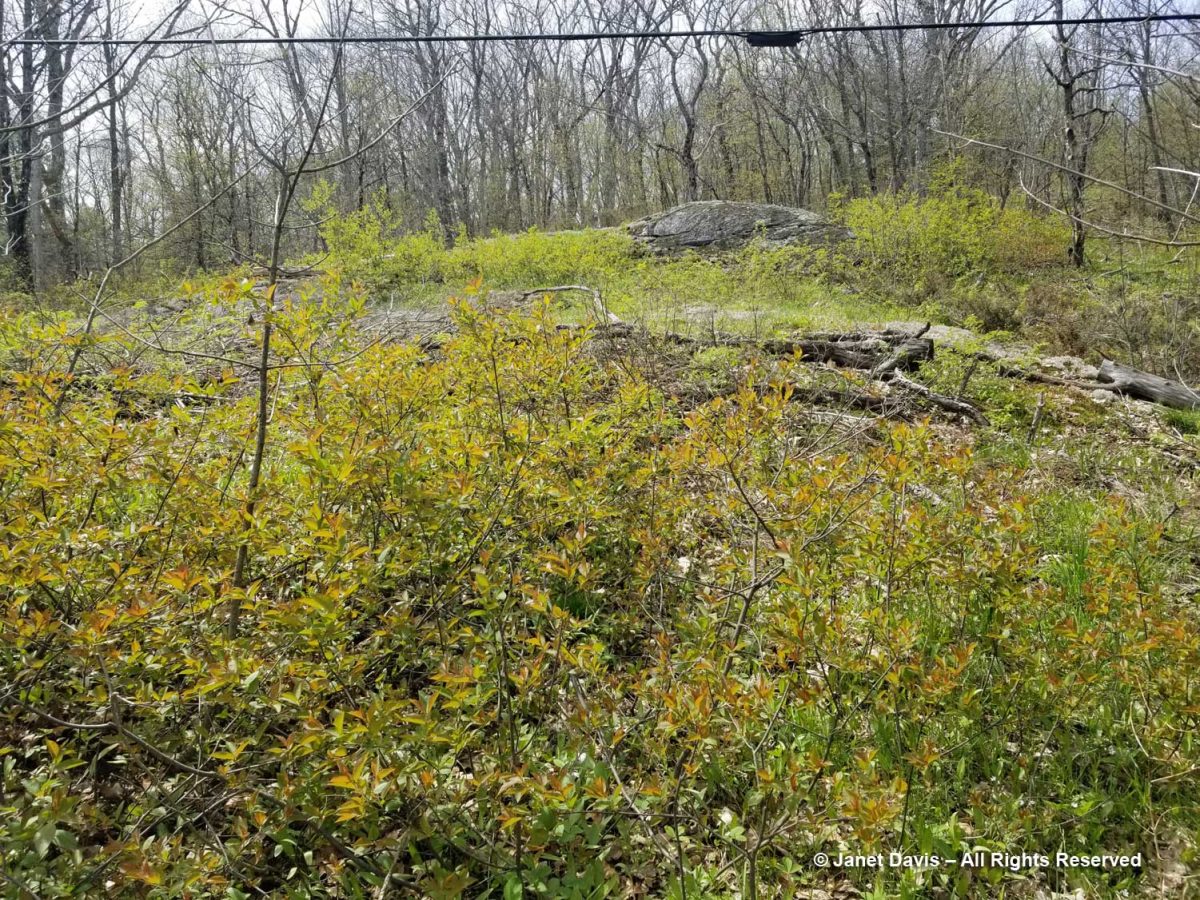
It was at this point that we left the road and walked towards a rocky outcrop about 30 feet away. Maintaining the overhead hydro line here requires tree and brush cutting that provides a little more light than normal……

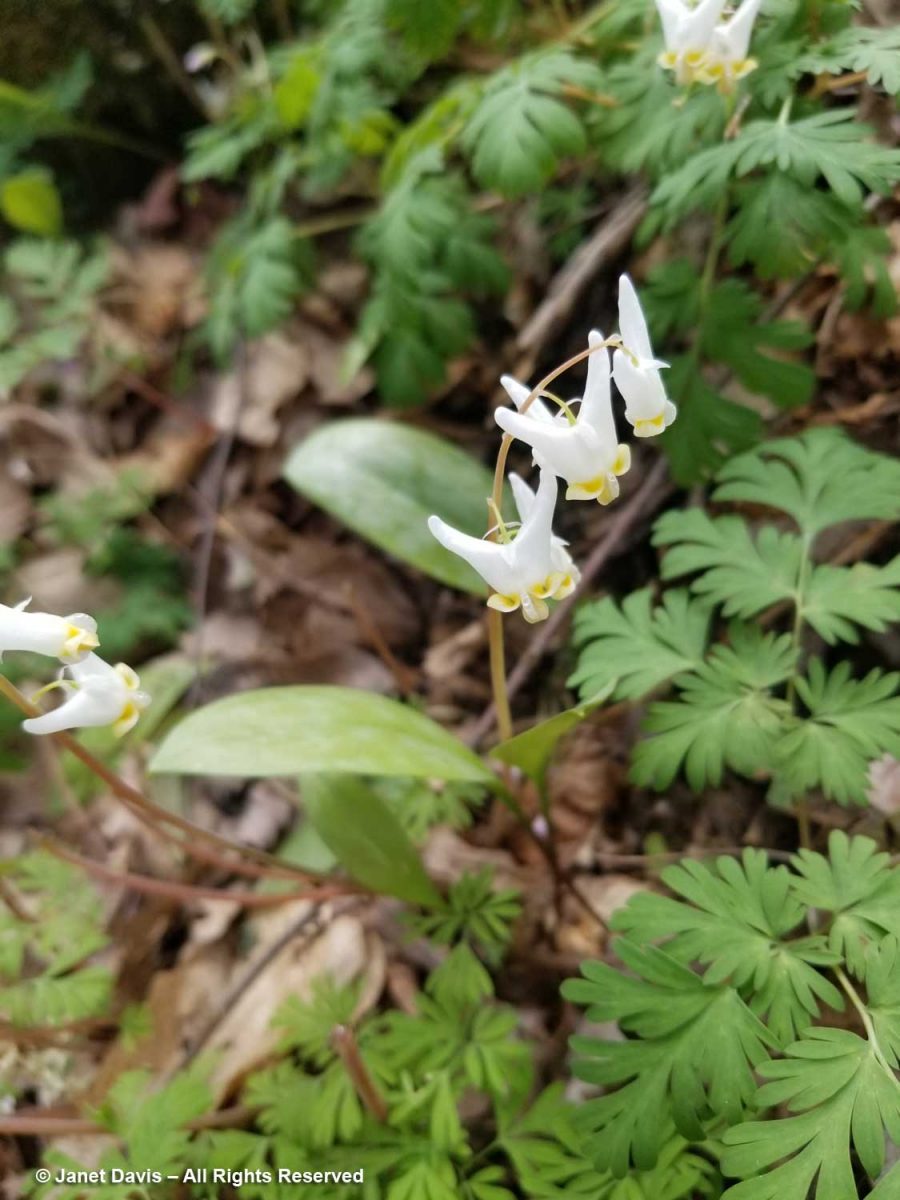
……and this area was rich with loads of spring ephemeral Dutchman’s breeches (Dicentra cucullaria)….

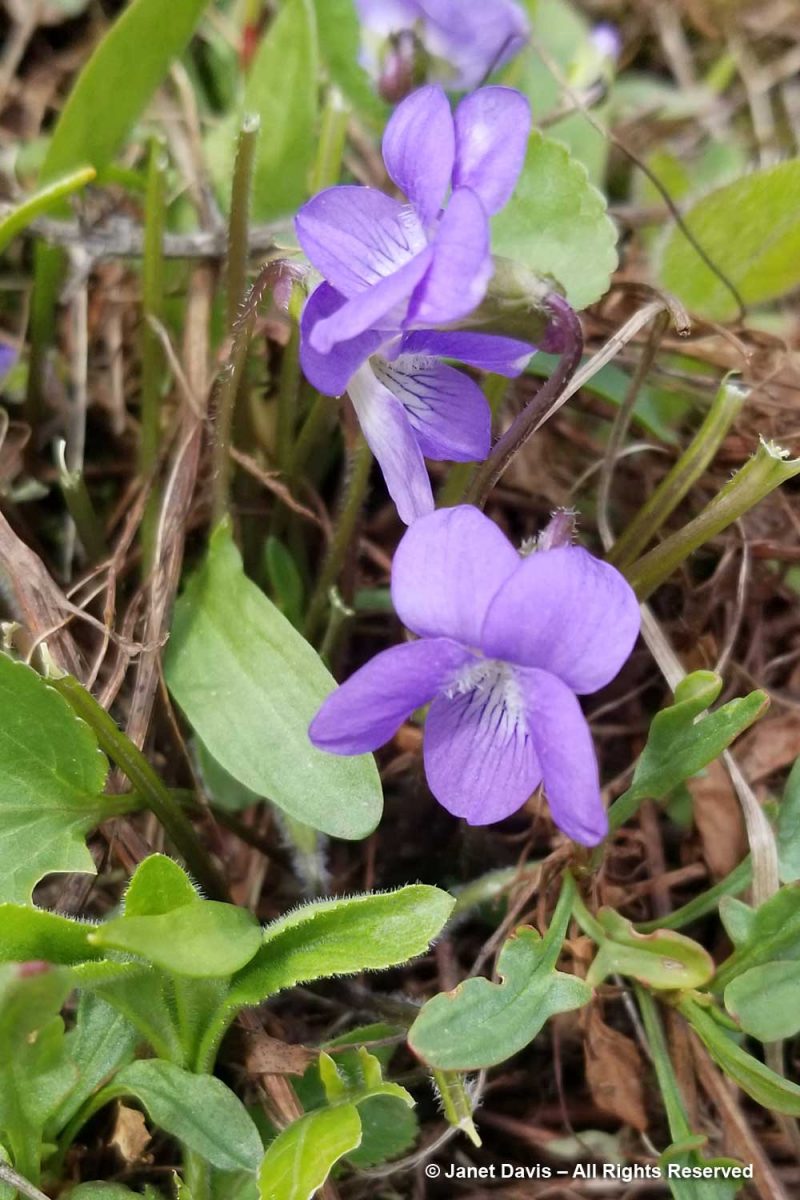
…. and the occasional common blue violet (Viola sororia).

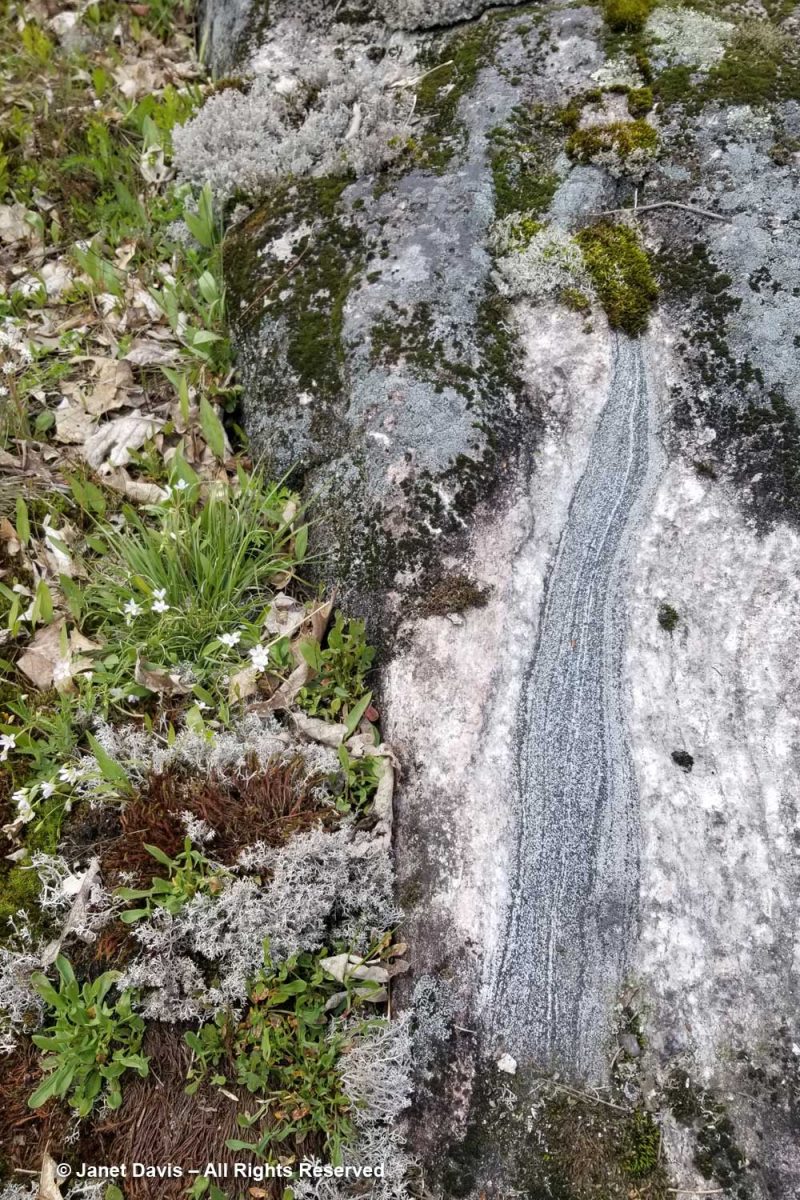
I loved this exposed bit of rock, typical of the metamorphic banded gneiss on this part of the Canadian Shield, a remnant of the Grenville Orogeny and more than a billion years old. (If you want a lot more amateur geology, have a peek at my recent blog memoir, ‘My Jaded Past, My Rocky Present’).

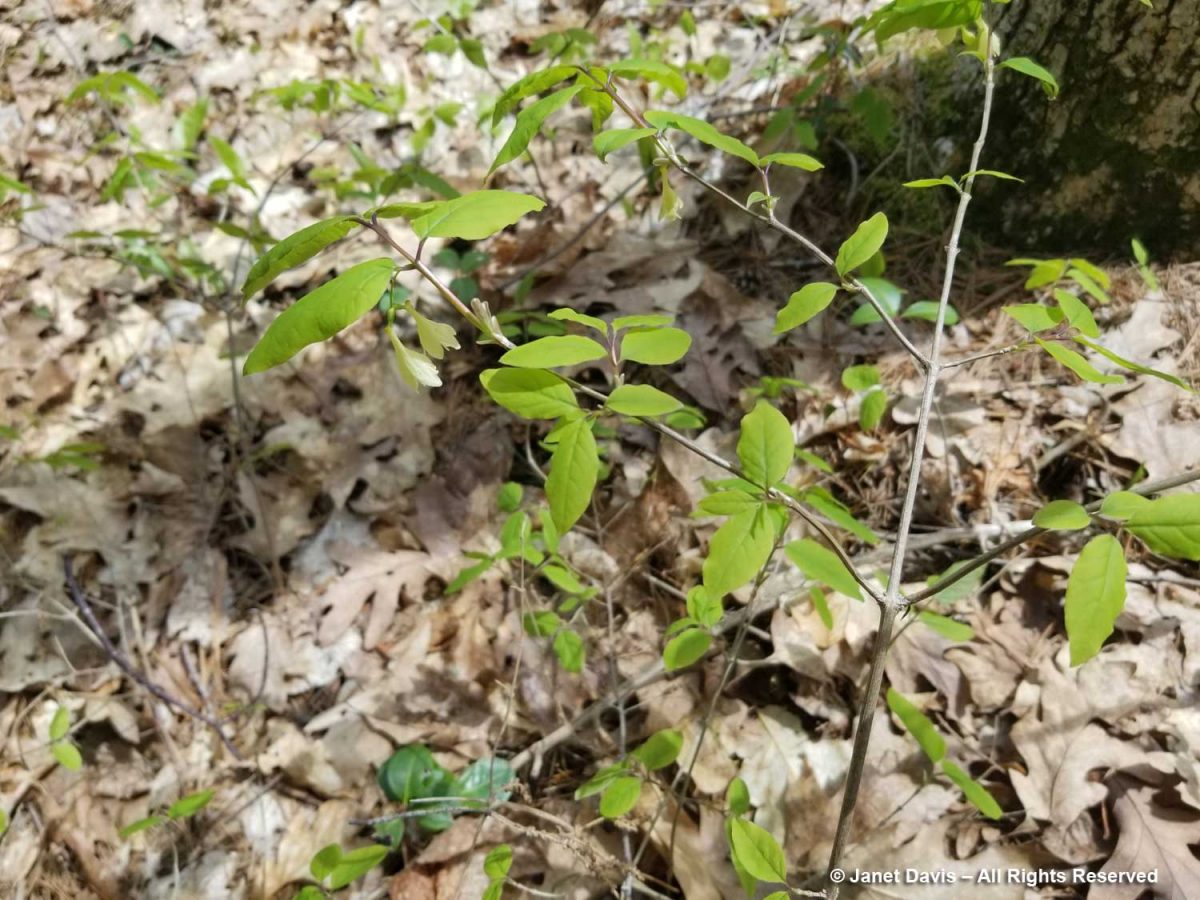
I spotted an unfamiliar shrub on the lake side of the road and wandered in to check it out. It was American fly honeysuckle (Lonicera canadensis) with its paired, pendant, pale-yellow flowers.

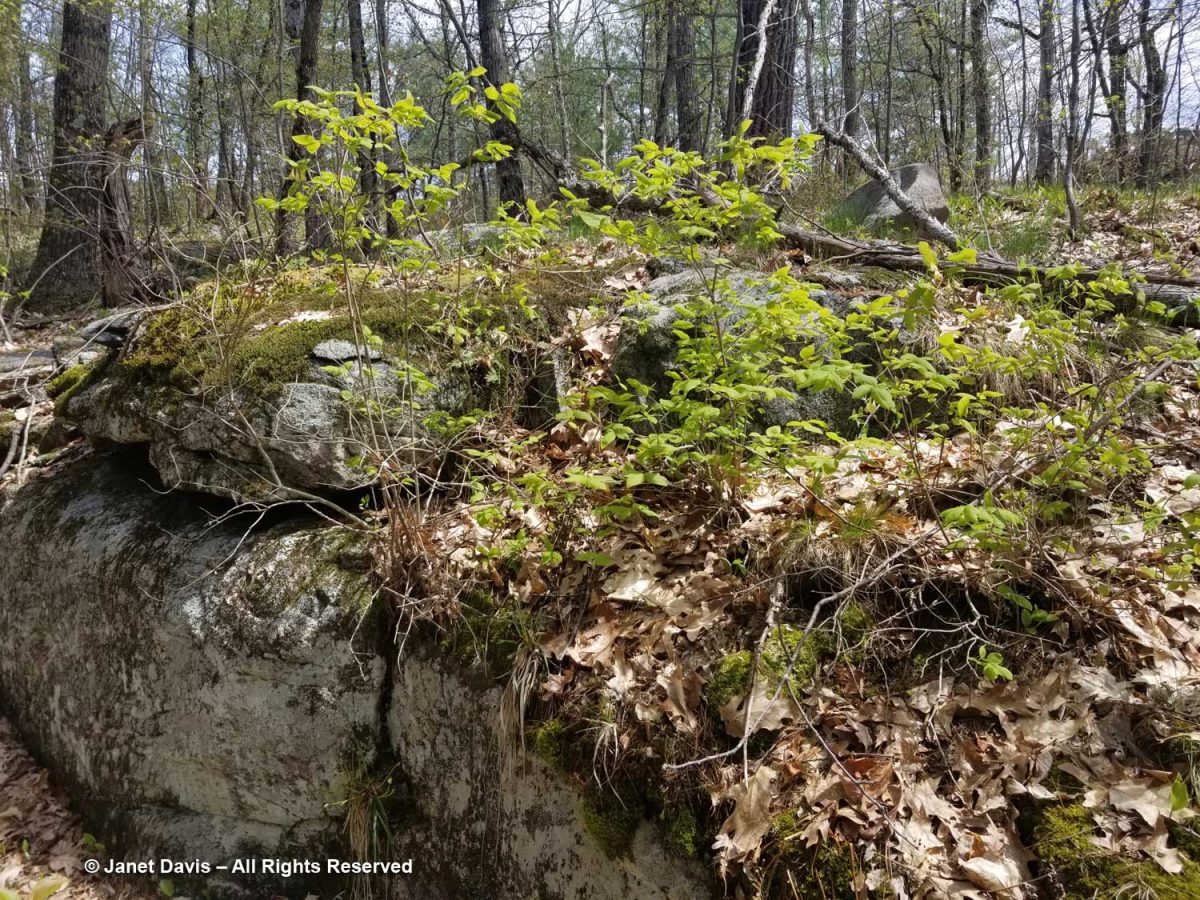
The shrubs grew on top of the outcrop nearby – not showy, but an integral part of the ecosystem.

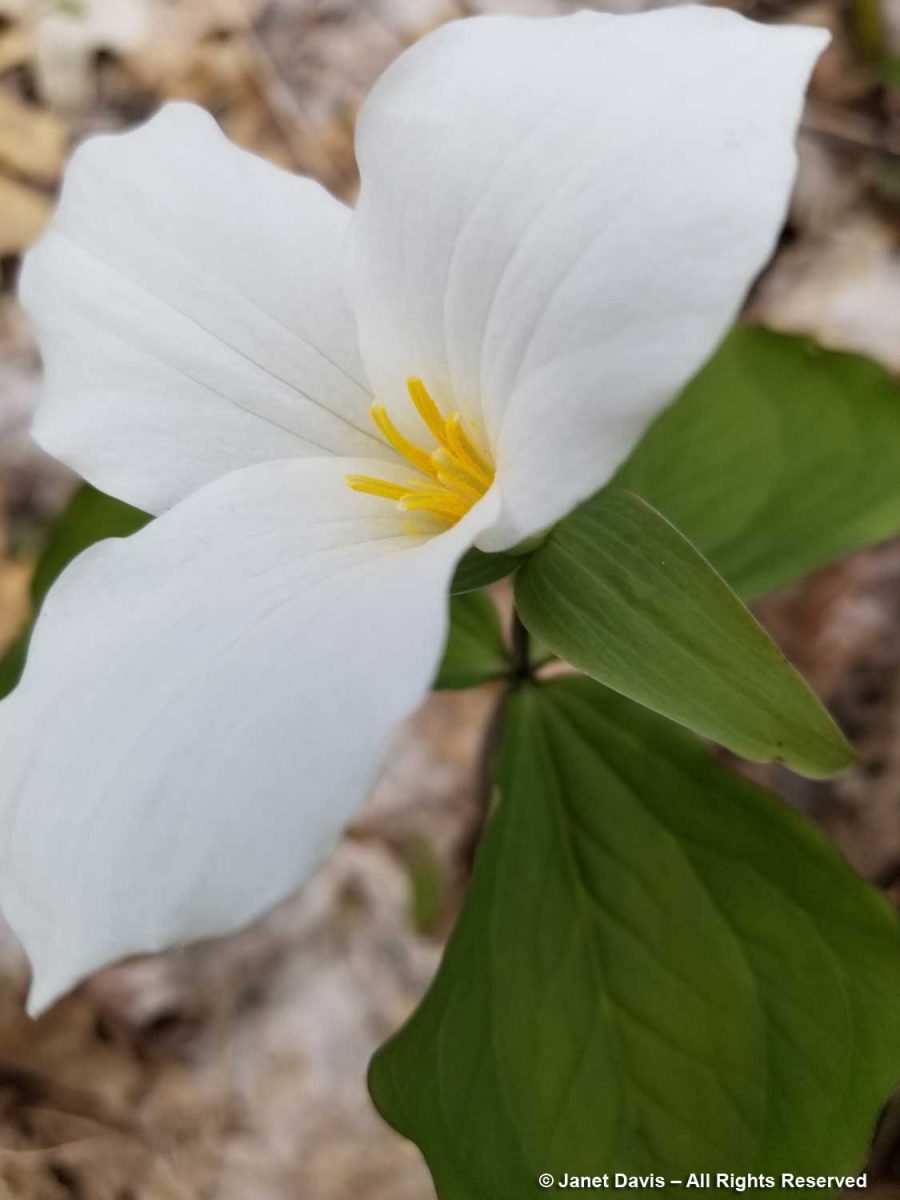
Finally, as we got close to the back of the East Bay Landing property, there were trilliums (T. grandiflorum). Not the vast colonies we would see on rises along Highway 38 and 400 later, just a few here and there with lots more getting set to bloom.
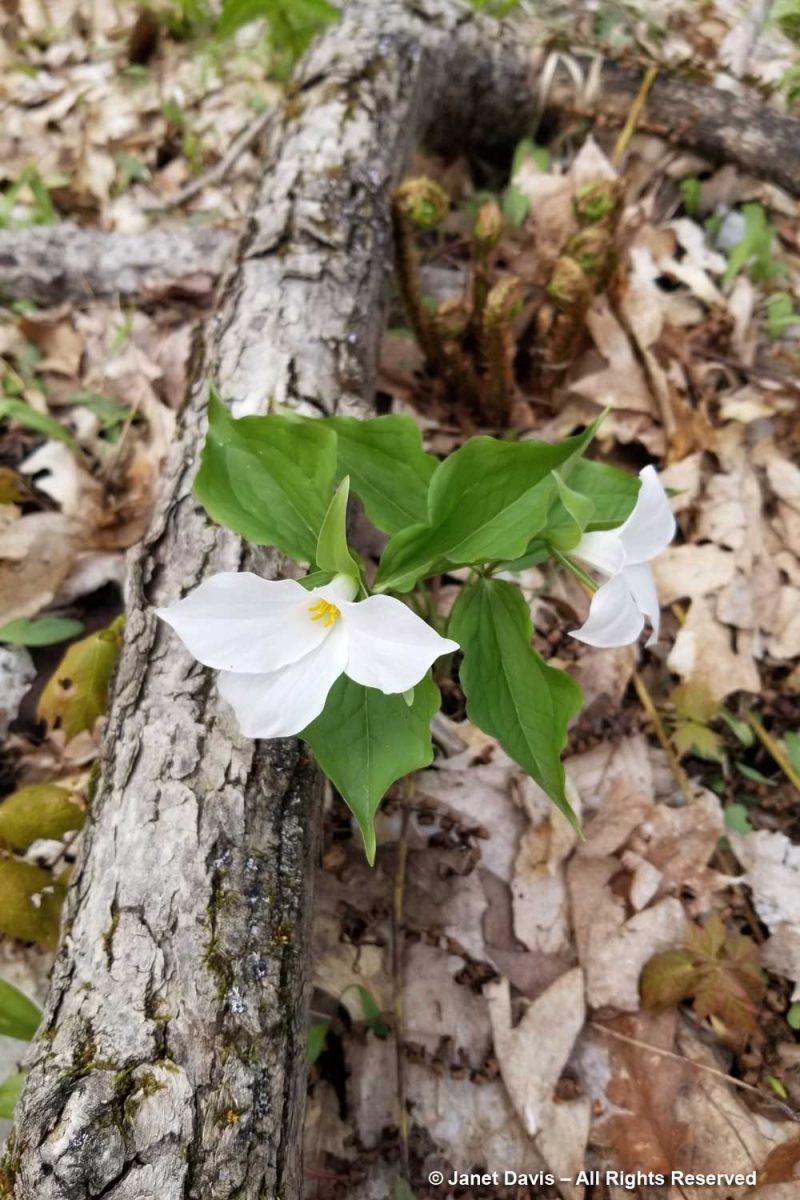

It was the perfect way to end our walk into the May woods on Lake Muskoka.

