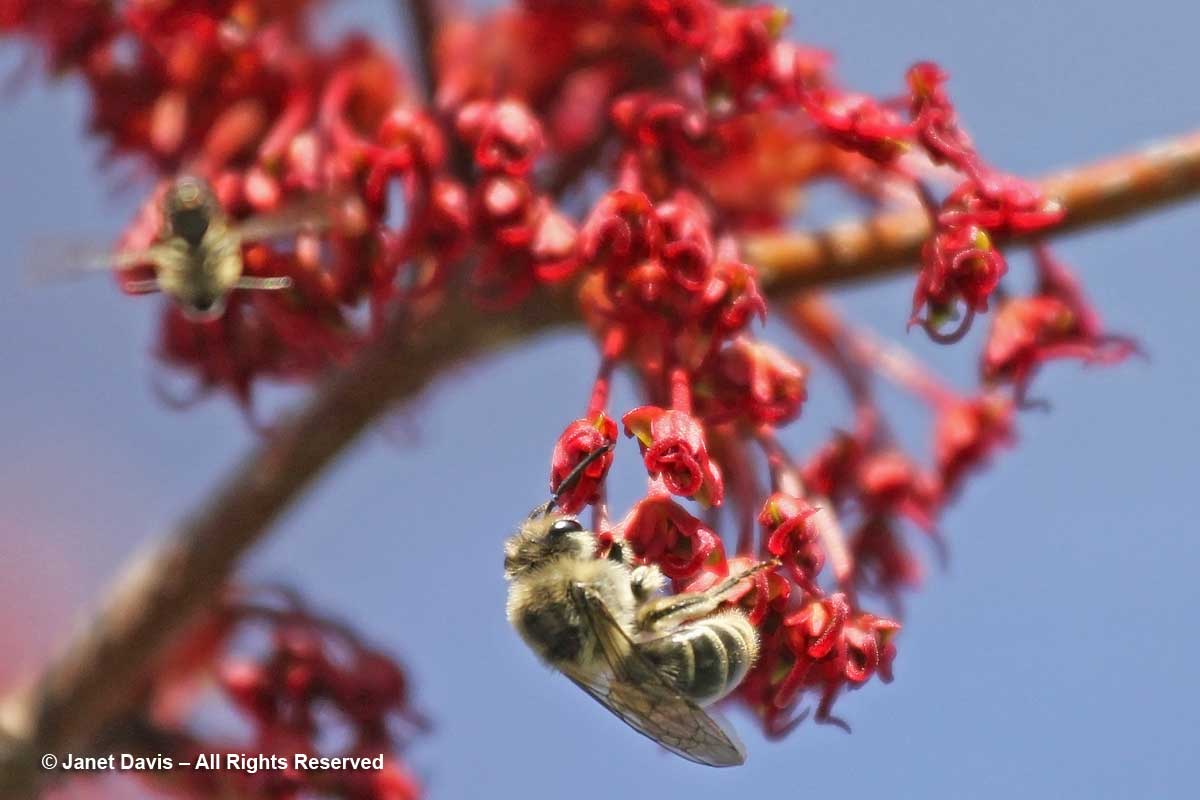
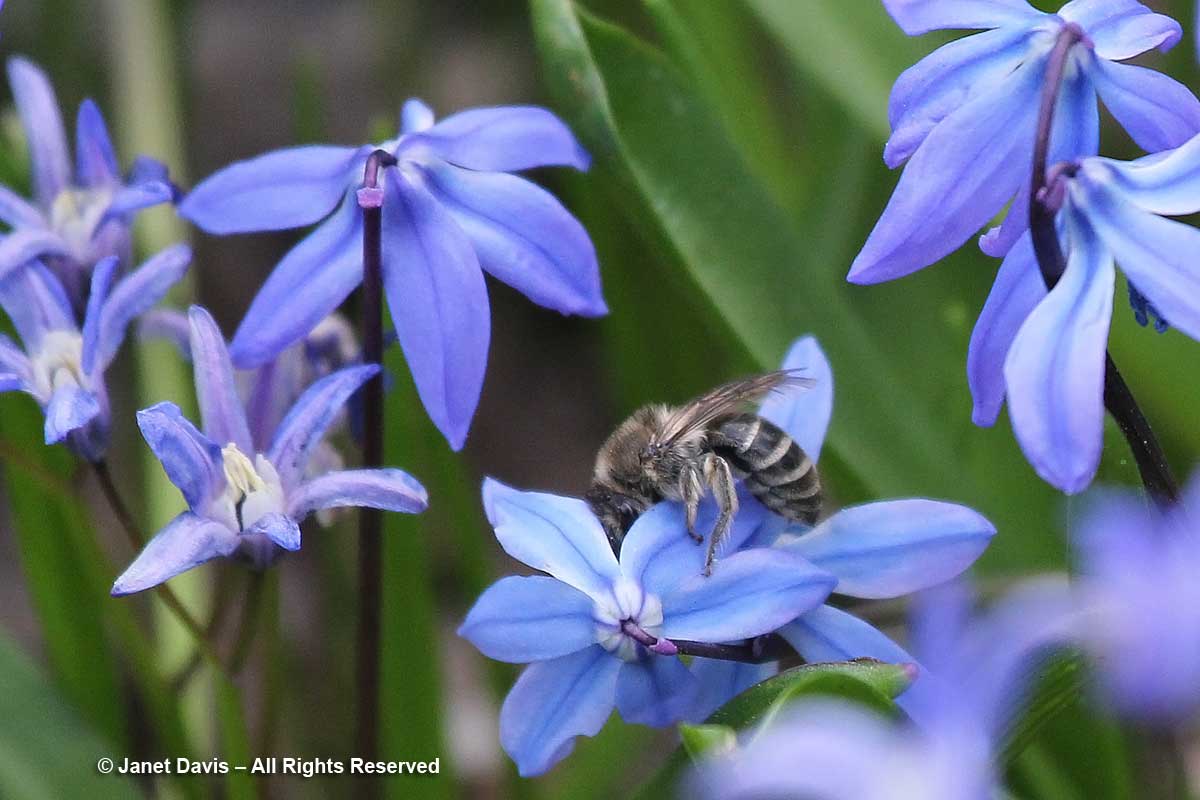
My front garden in Toronto is filled at the moment with hundreds of native cellophane bees, Colletes inaequalis. Sometimes called Eastern plasterer bees or polyester bees (and grouped generally with mining bees), they get their common name for the viscous, waterproof, transparent substance (sometimes compared to plastic wrap) that the females secrete to line and seal the brood cells they burrow in the ground. Their species name means “unequal”, and refers to the unequal segments of the right and left antennae. They’re one of the earliest bees to emerge in spring and can often be seen on April-flowering native red maples (Acer rubrum), like the one below in Toronto’s Mount Pleasant Cemetery…..
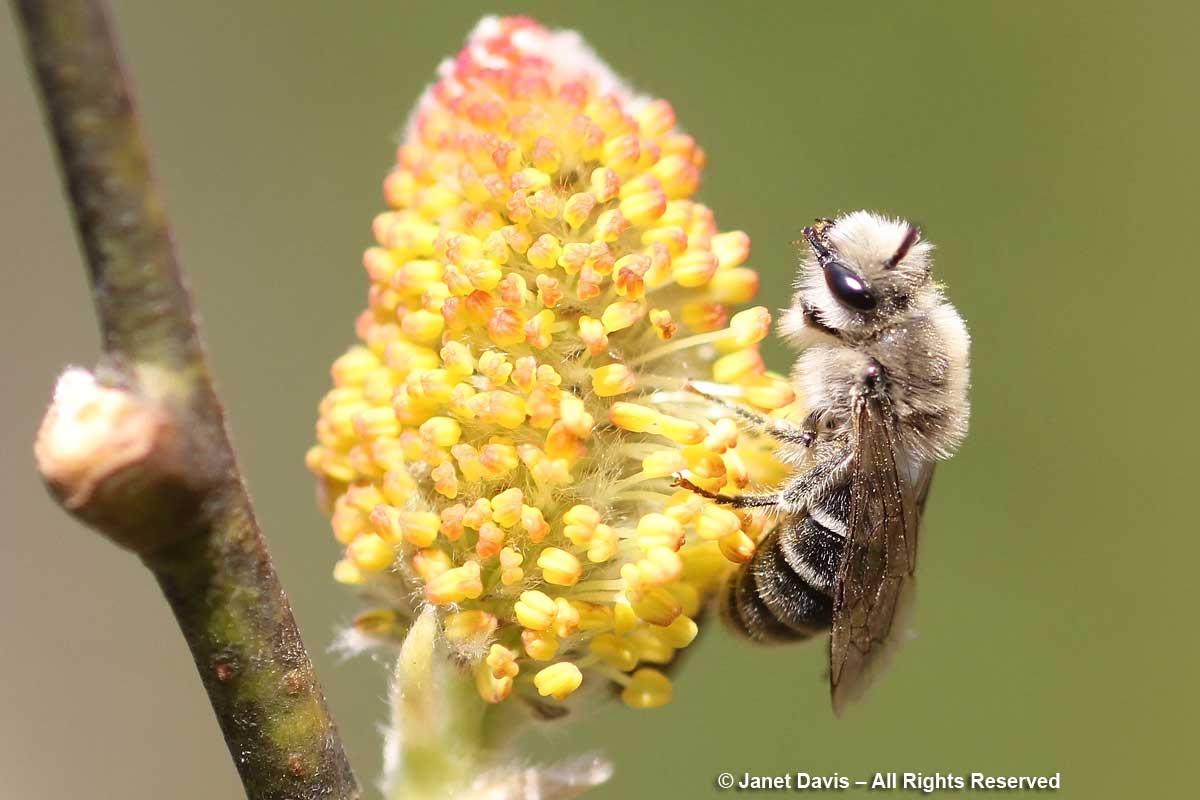
…. and pussy willows (Salix discolor), also in the cemetery.
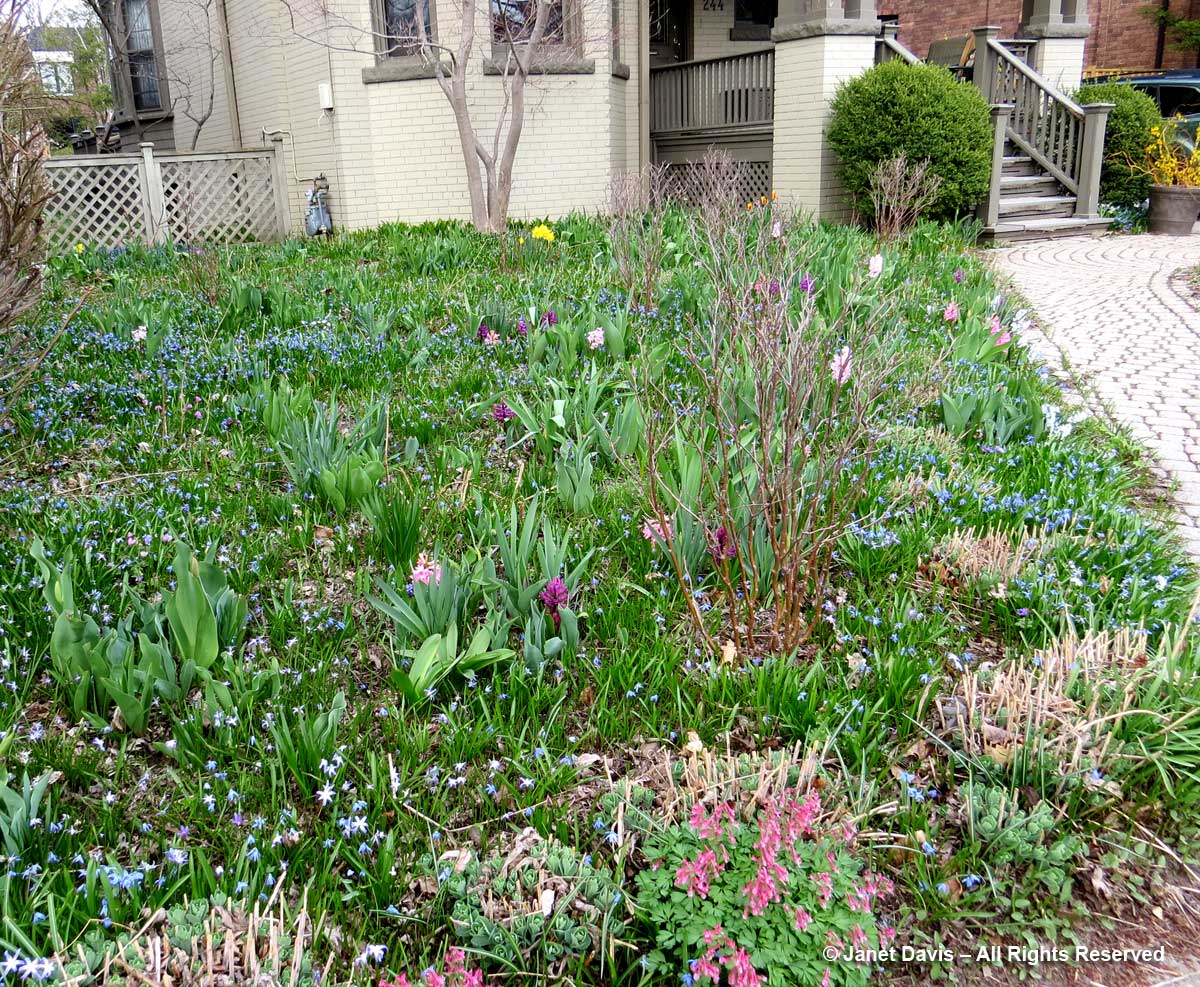
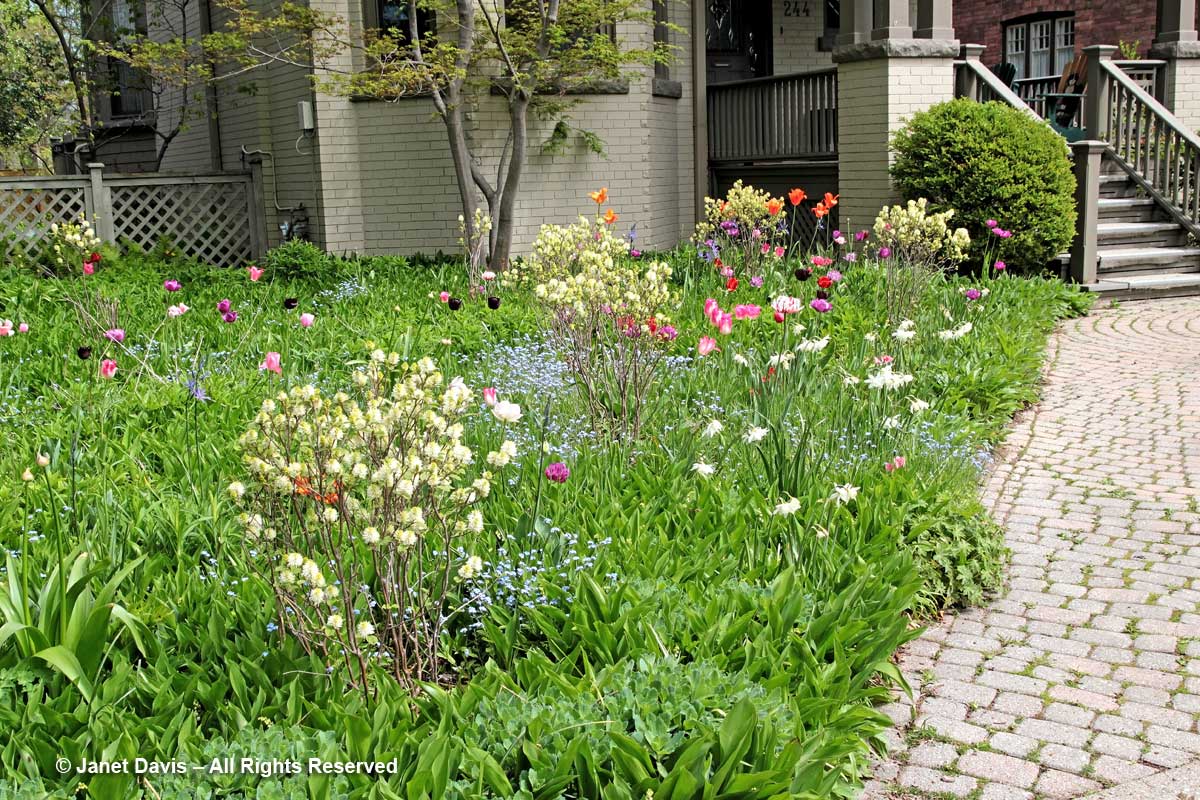
My front garden is also filled with the little blue flowers of the non-native, spring-flowering bulb Siberian squill, Scilla siberica.
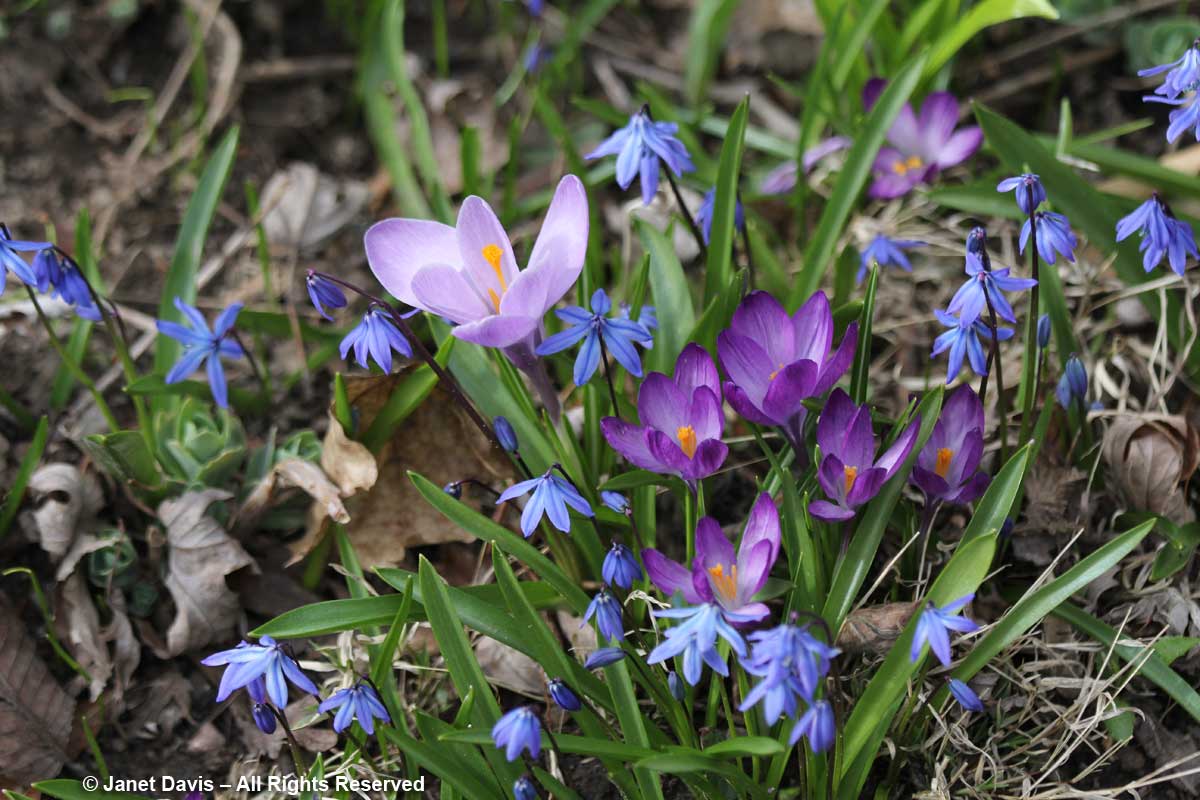
They’ve been slowly spreading there for at least 20 years, probably much longer, since we’ve been in our house for 33 years and it was soon after I saw the “blue lawns” in our neighbourhood that I decided to plant a few of the little bulbs. Needless to say, the scilla likes our slightly alkaline clay. Quite a lot! Though considered invasive, they are not listed as a serous threat, like Japanese knotweed and dog-strangling vine, since they occupy fairly specific niches and disappear after the foliage ripens. In my garden, they emerge with the crocuses…..
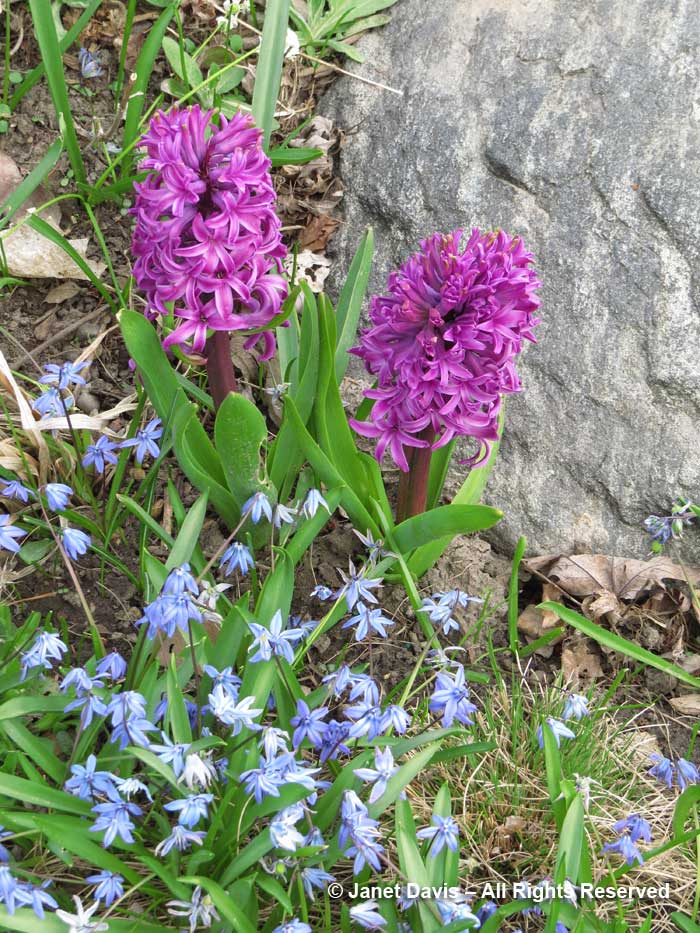
….. and stay in bloom for the fragrant hyacinths…
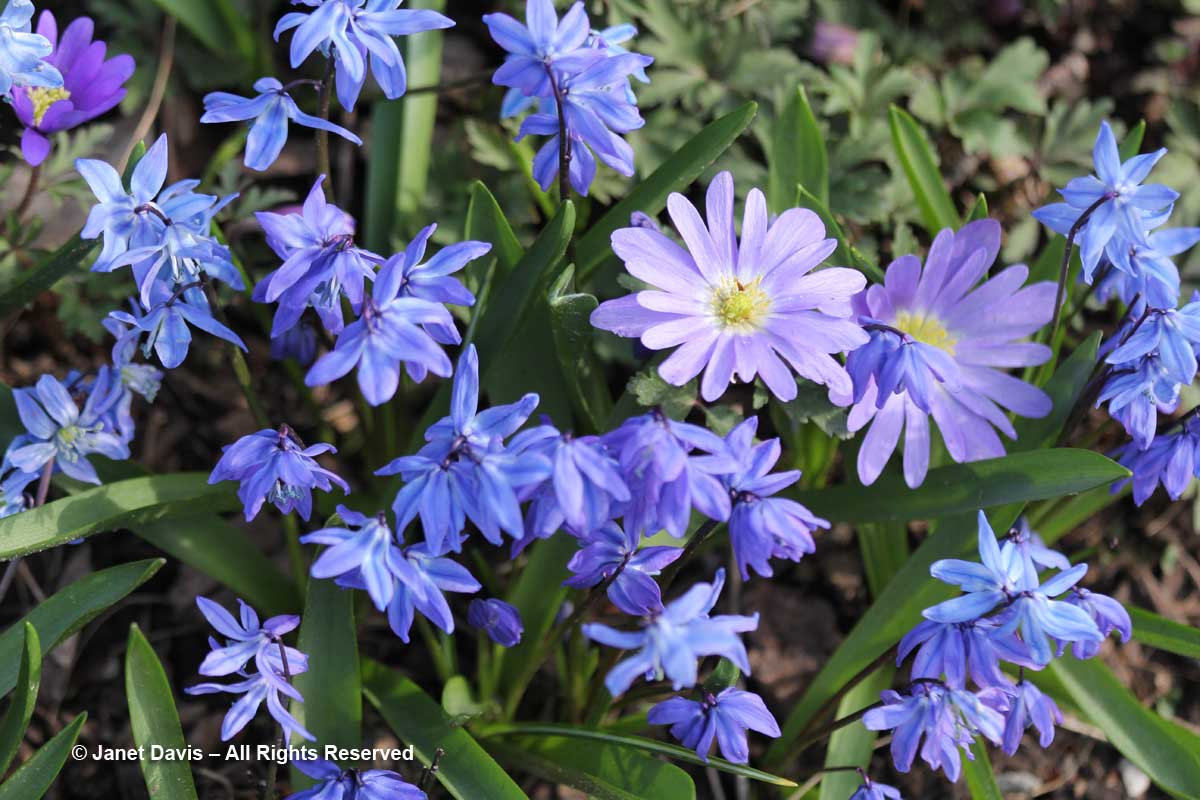
….. and windflowers (Anemone blanda)….
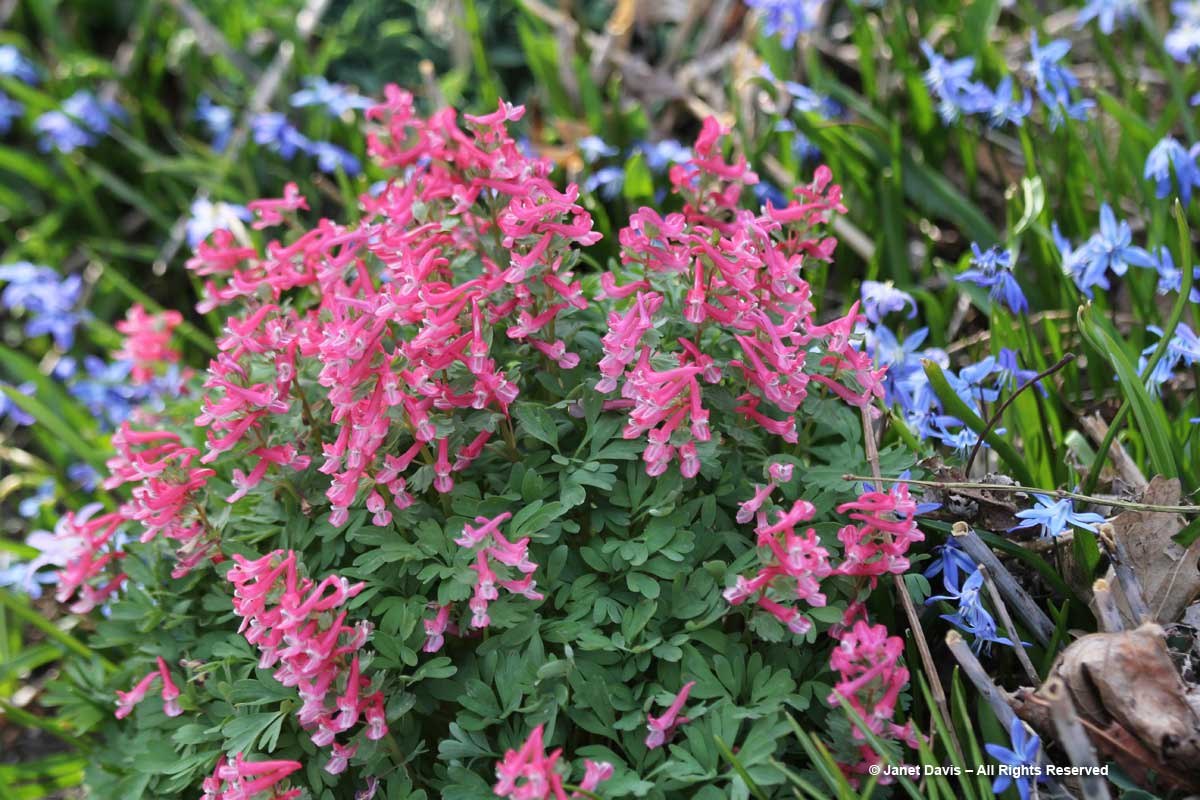
And Corydalis solida ‘George Baker’
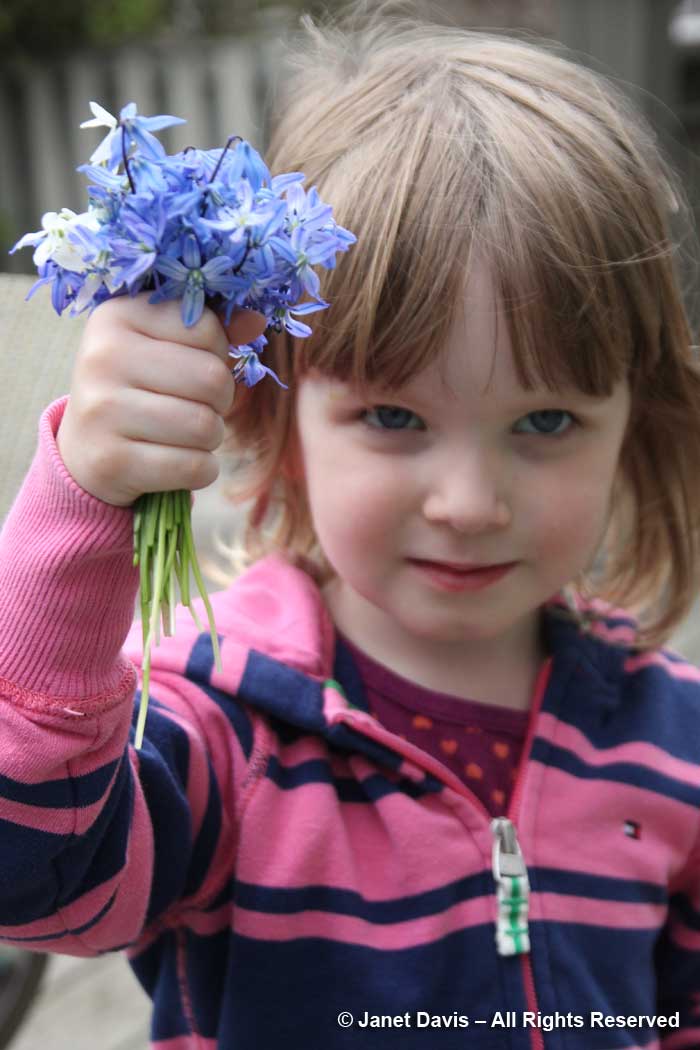
There are thousands enough that my little granddaughter is free to pick handfuls of them.
Later, my front garden will be filled with daffodils, tulips and the bottlebrush flowers of Fothergilla gardenii.….
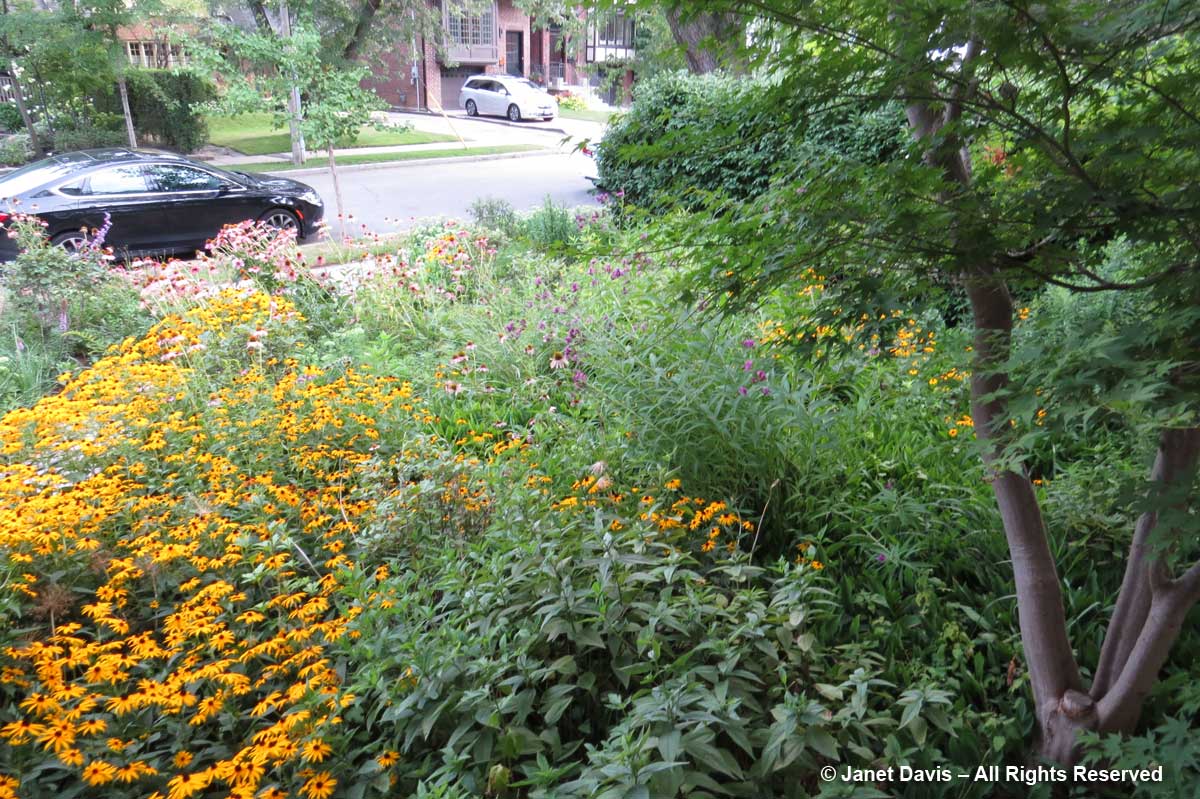
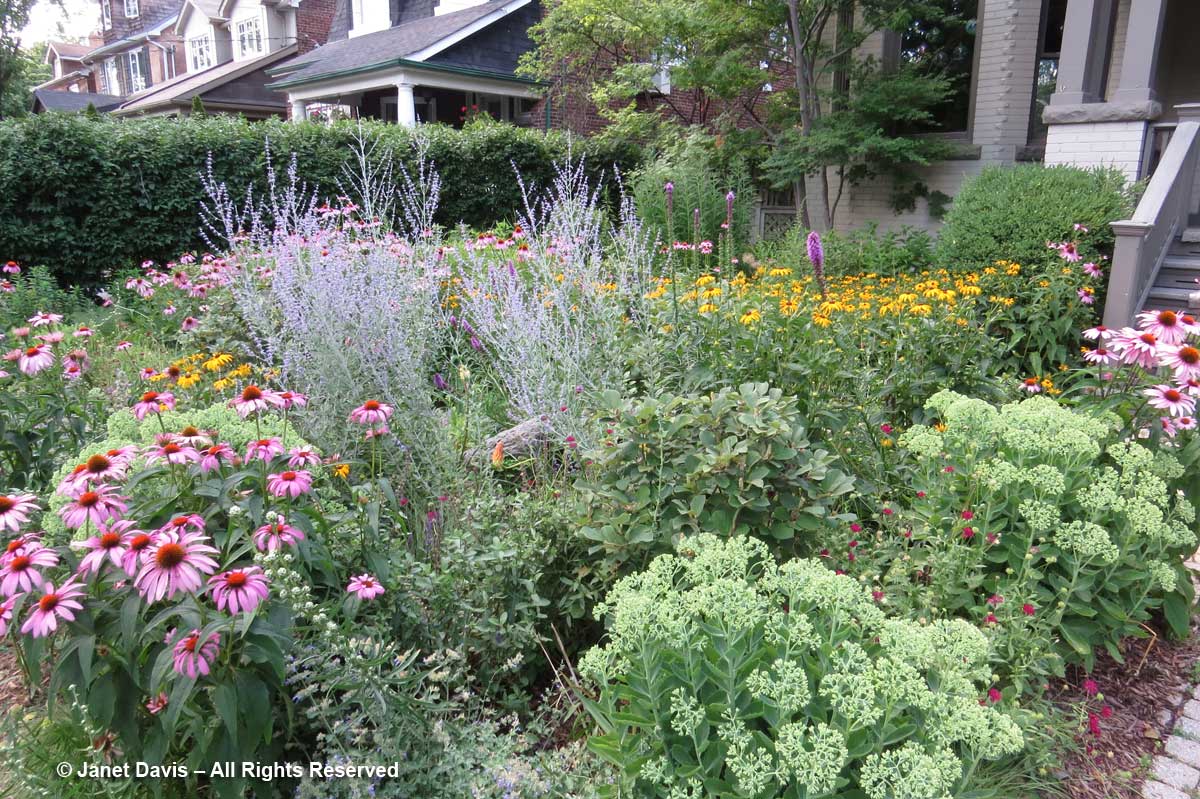
….and later still, sun-loving North American (not necessarily Ontario) prairie natives like echinacea, rudbeckia, liatris, vernonia and aster, chosen for their appeal to native pollinators.
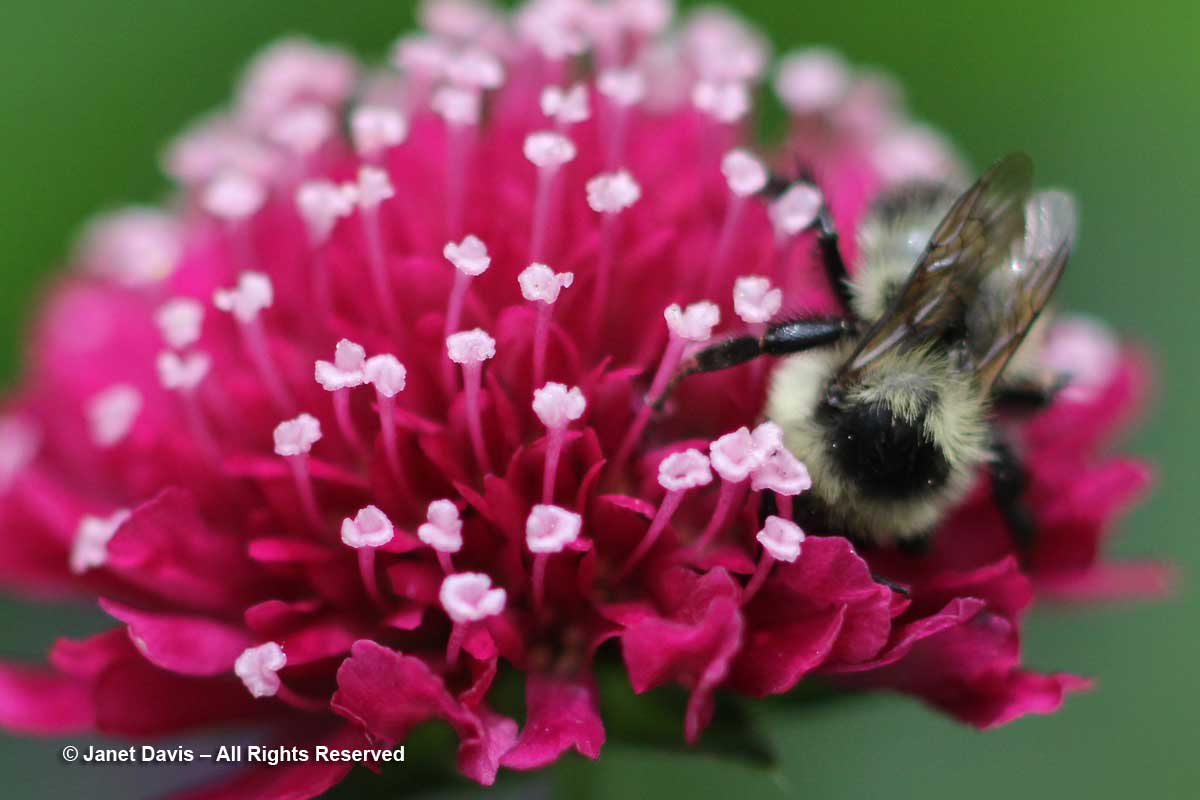
I also grow many non-native plants like meadow sage (Salvia nemorosa), catmint (Nepeta racemosa ‘Walker’s Low’), Russian sage (Perovskia atriplicifolia) and Knautia macedonica and sedums, also chosen for their appeal to native pollinators….
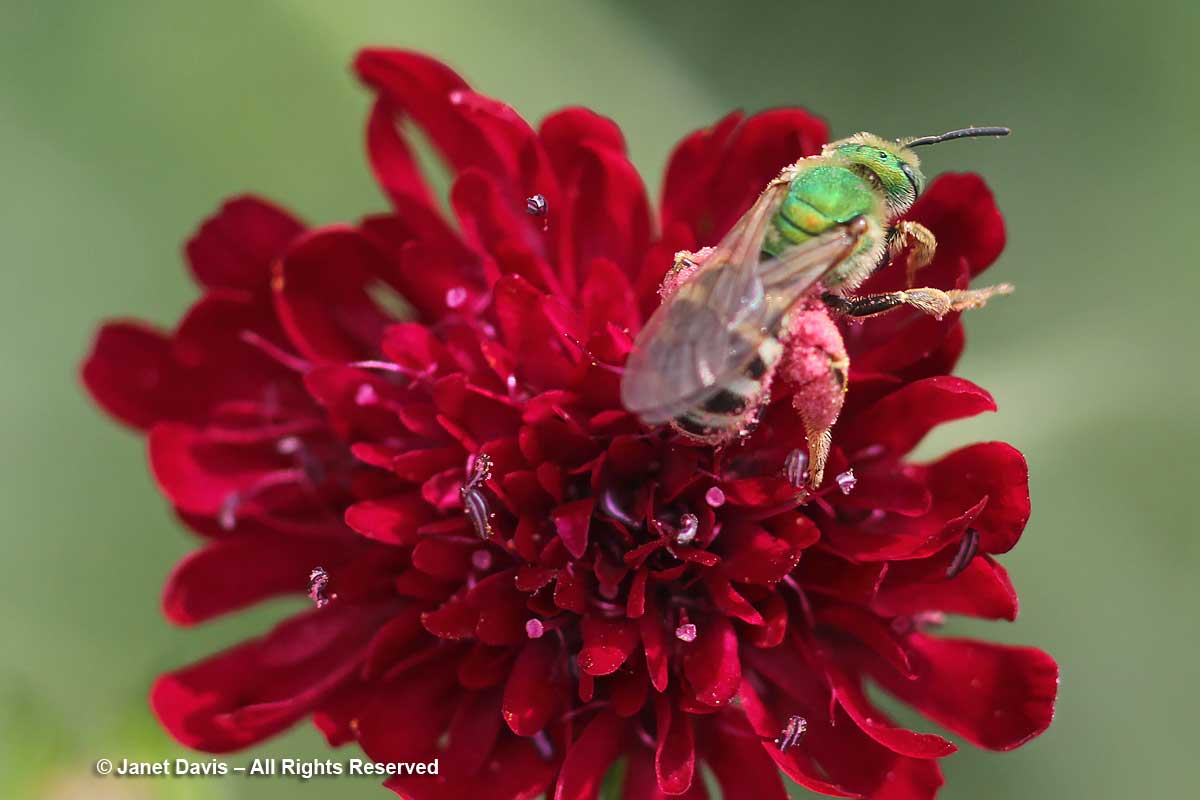
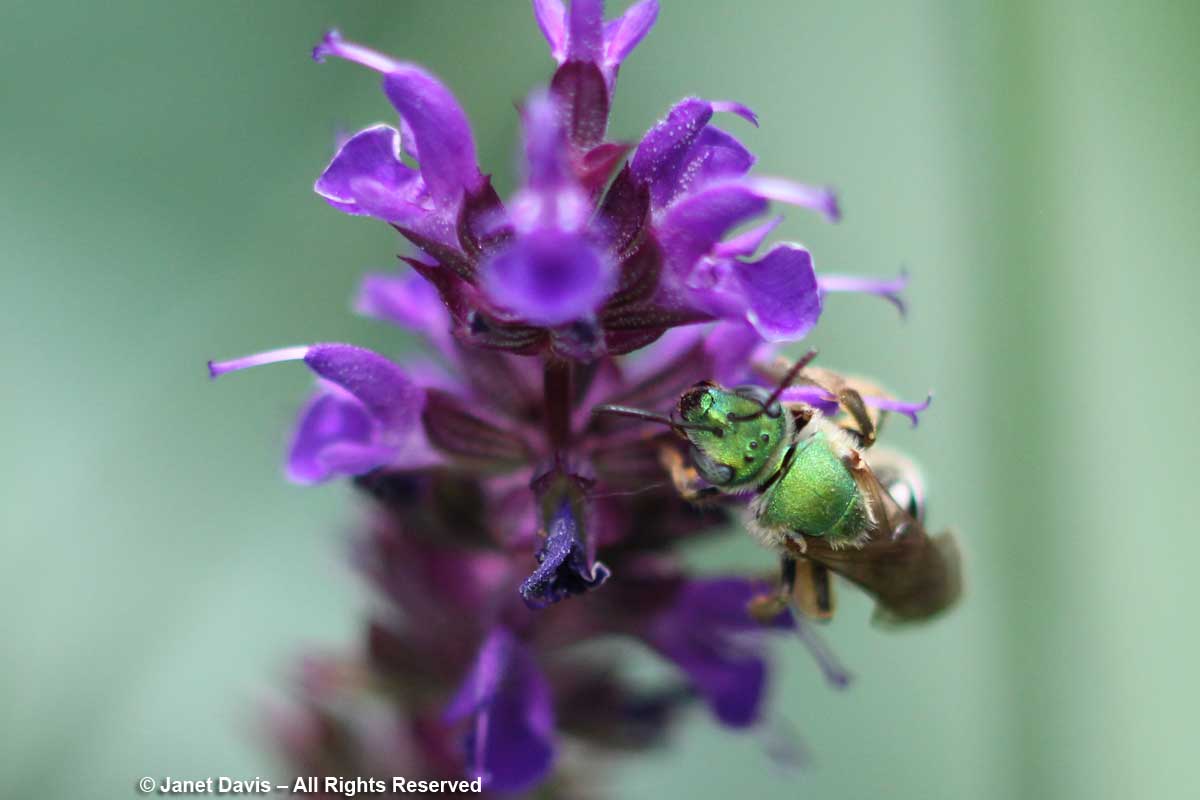
…. like the little native metallic sweat bee (Agapostemon virescens), here on knautia….
….and ‘Mainacht’ meadow sage…
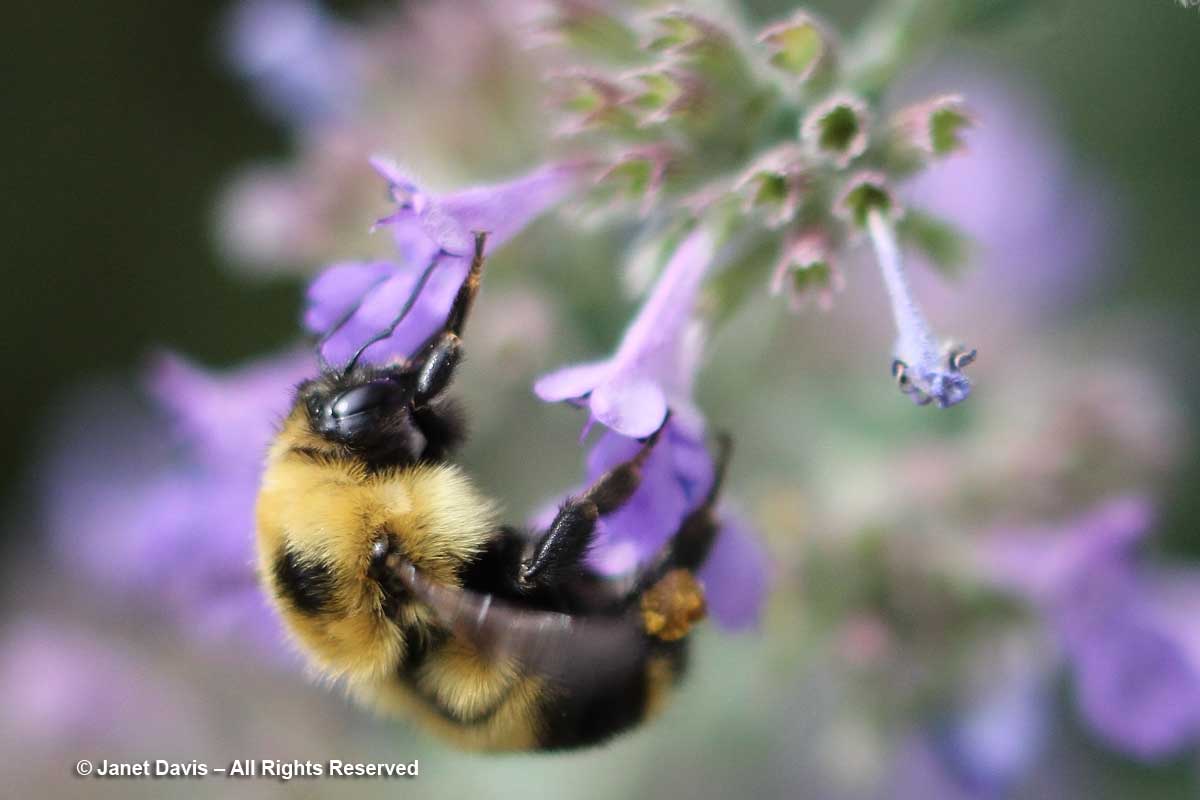
….and native bumble bees of all kinds, here on knautia….
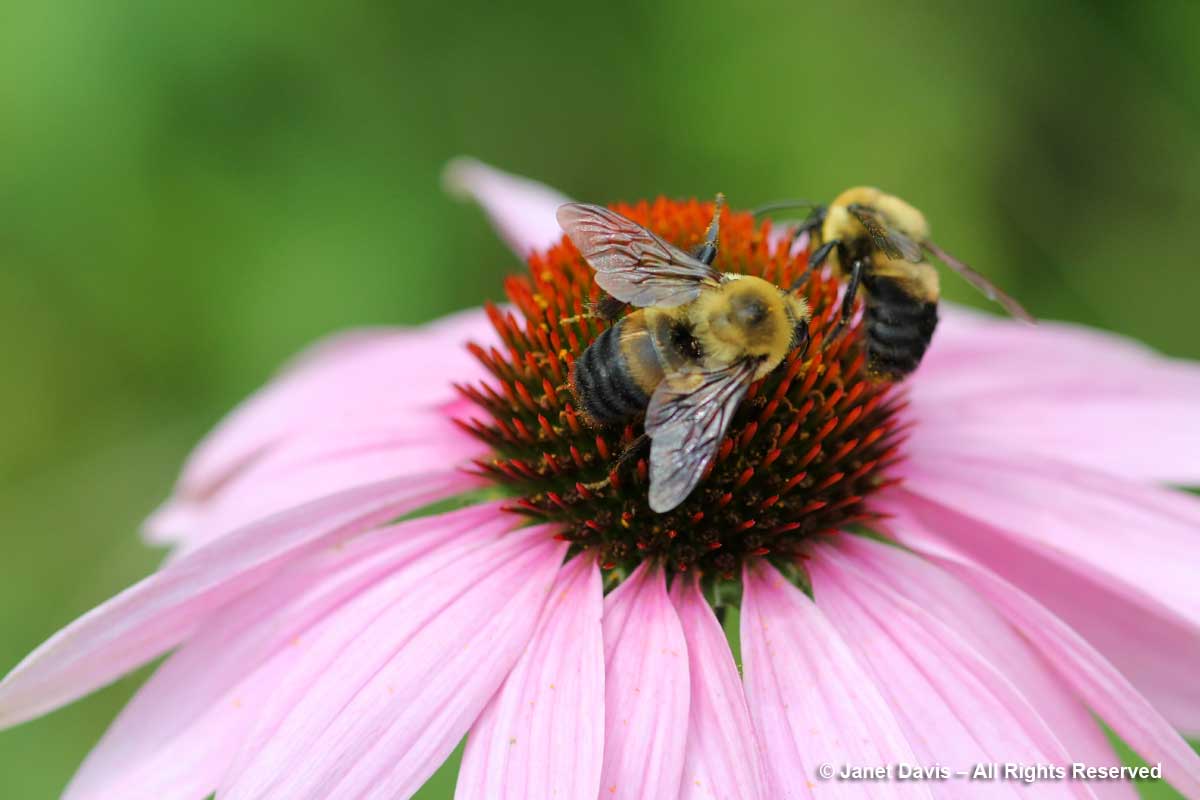
….. and later in the season on echinacea…
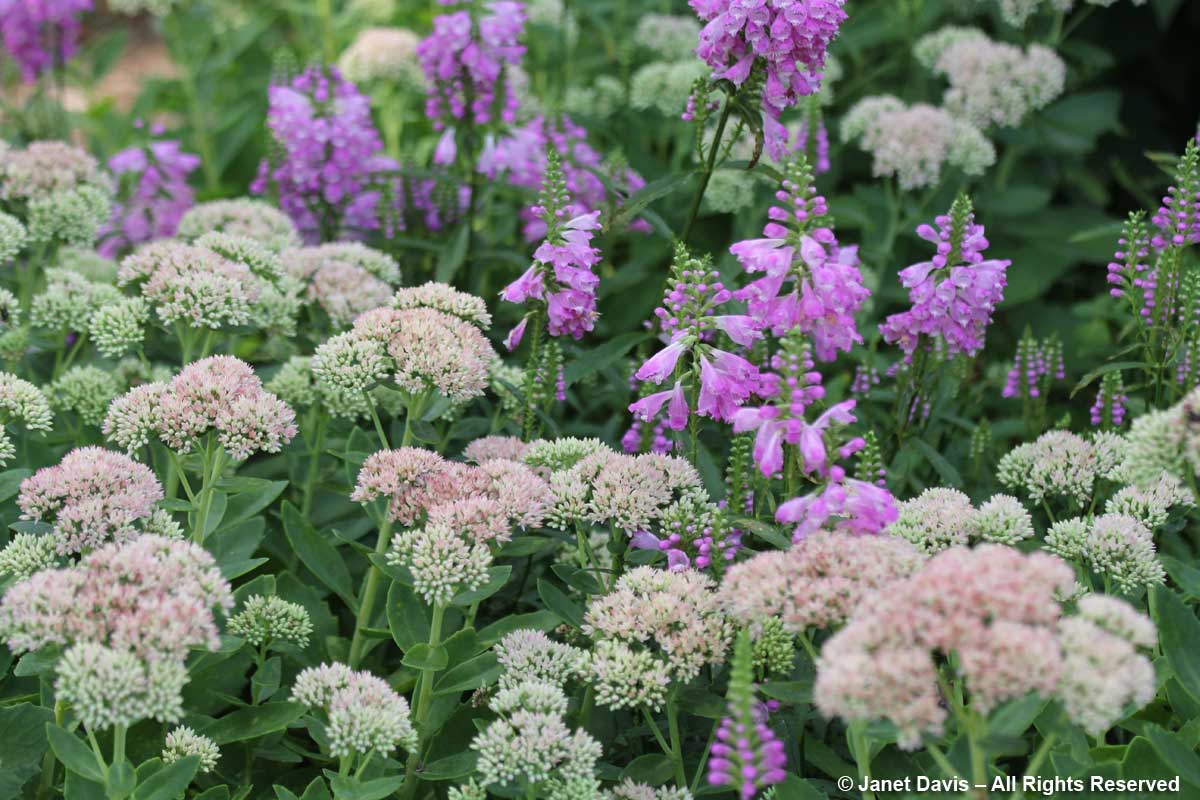
In late summer and autumn, there’s a mix of non-native sedum ‘Autumn Joy’ and native obedient plant (Physostegia virginiana).
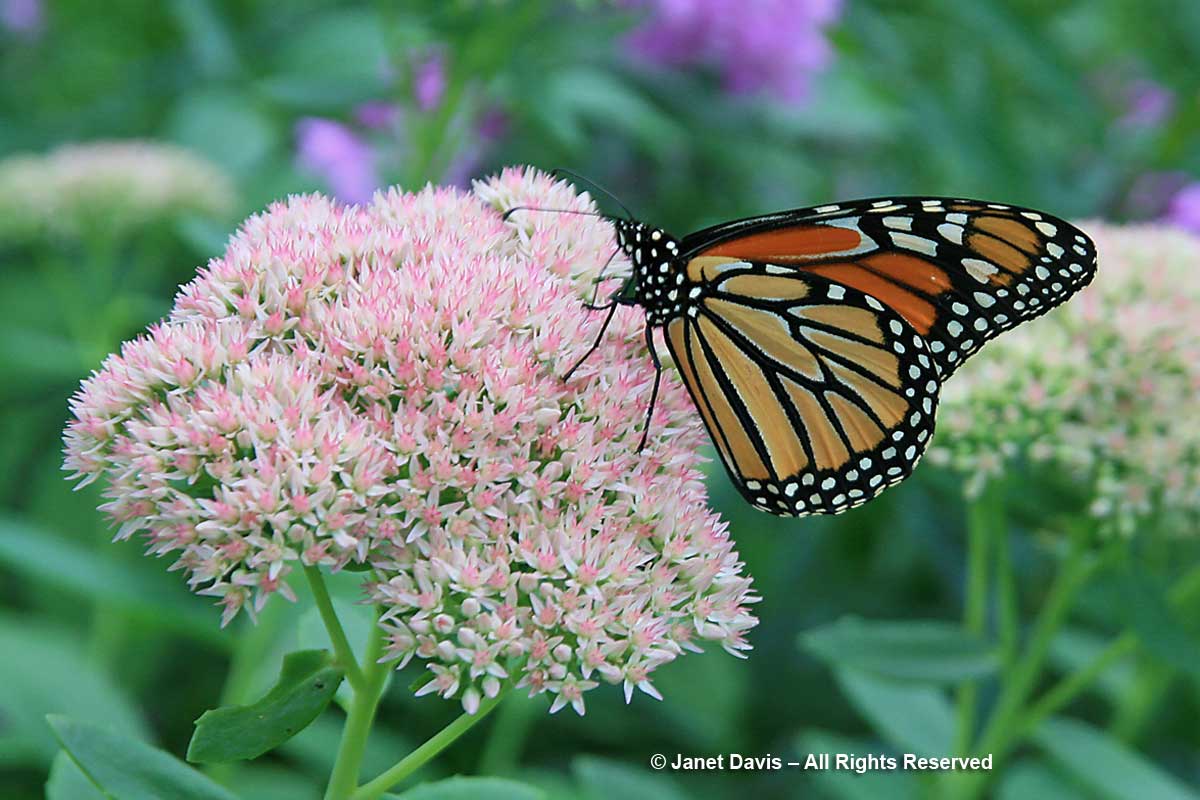
Monarch butterflies congregating in Toronto before the long flight over Lake Ontario as they migrate to Mexico adore the sedums (as do bumble bees and honey bees)…..
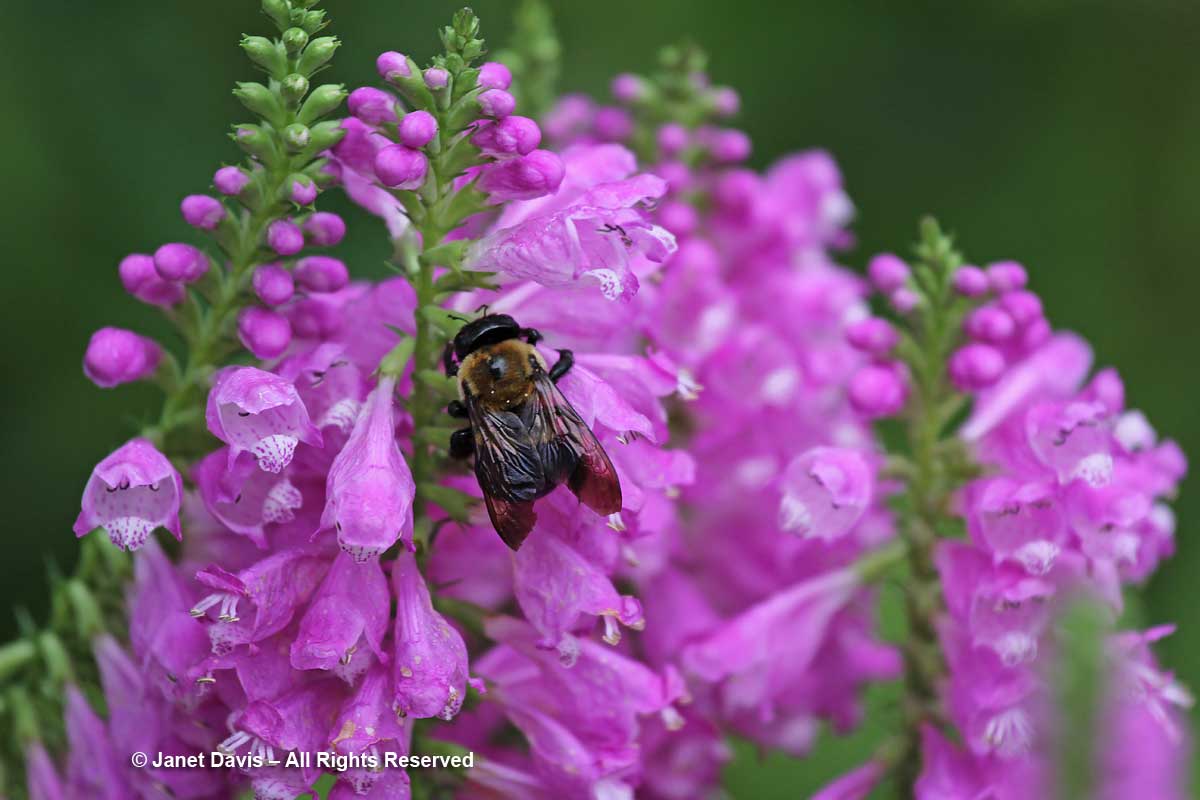
….. and native carpenter bees (Xylocopa virginica) do some clever nectar-robbing to get at the nectar in the corollas of the obedient plant.
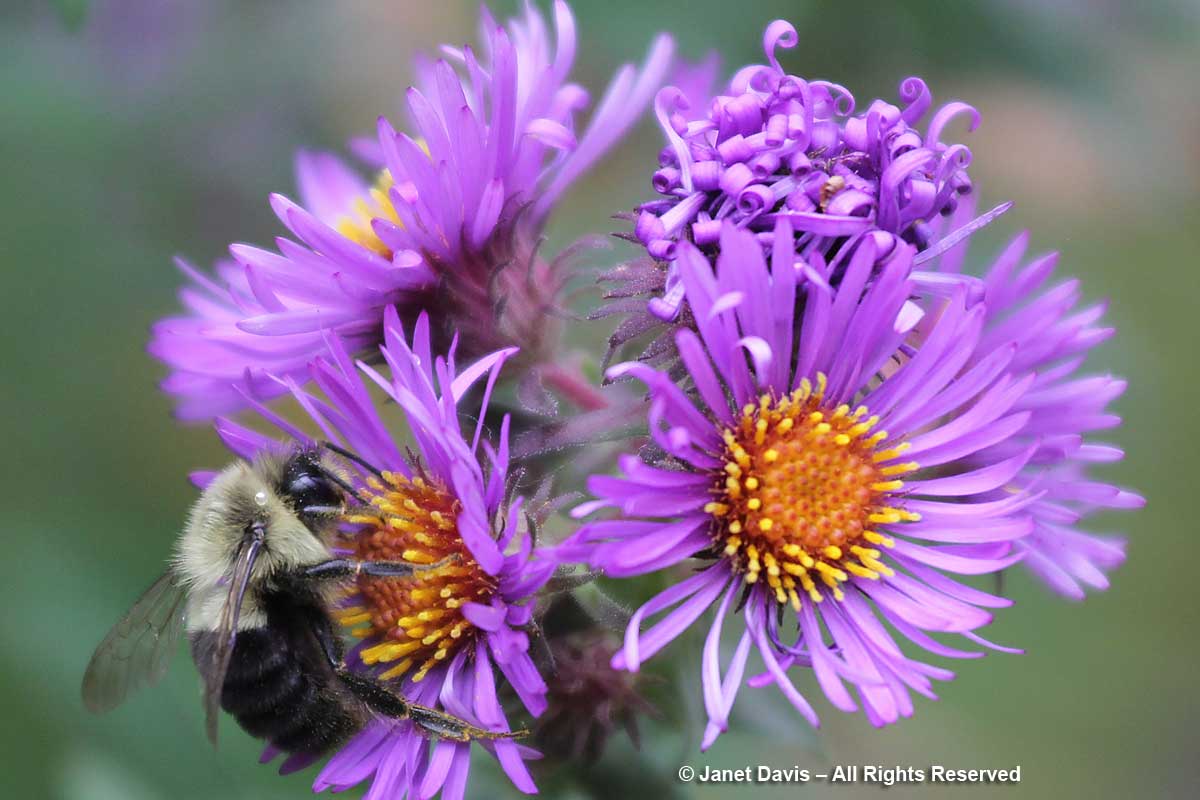
The final chapter in my front garden consists of native goldenrod and rich purple New England aster, below, both valuable to native pollinators.
***************
But back to my garden in April. The little blue Siberian squill is why the native bees are there. Cellophane bees are a vernal species. As noted in this excellent bee brochure from the City of Toronto , “As soon as the weather becomes warm enough in late March or April, Common Eastern Plasterer Bees start emerging from their overwintering burrows in the ground. Males cluster around virgin females that are digging upwards to reach the soil surface and the mayhem that ensues can sometimes result in some bees being killed in the crush. Once they have mated, the female excavates a burrow in the ground, showing a preference for nesting in patches of bare, or sparsely vegetated, soil.”
Colletes inaequalis is a polylectic species, or a polylege, meaning it gathers pollen from a variety of native and non-native plants from early spring to mid-summer, when their life cycle ends. According to observers, the plants it has been observed using include Aesculus (buckeye, horsechestnut), Amelanchier (serviceberry), Anemone, Anemonella, Arctostaphylus, Aronia (chokeberry), Cercis (redbud), Claytonia, Crataegus (hawthorn), Dentaria, Dirca, Erythronium, Hepatica, Prunus (cherry), Ptelea, Pyrus (pear), Rhamnus (buckthorn), Rhus (sumac), Ribes (gooseberry, currant), Rubus (blackberry, raspberry), Salix (willow), Spiraea, Staphylea, Stellaria, Taraxacum (dandelion), Vaccinium (blueberry, huckleberry, myrtleberry, cranberry), Viburnum and Zizia. And in my garden, the unequal cellophane bee is the principal visitor to my thousands of non-native Siberian squill.
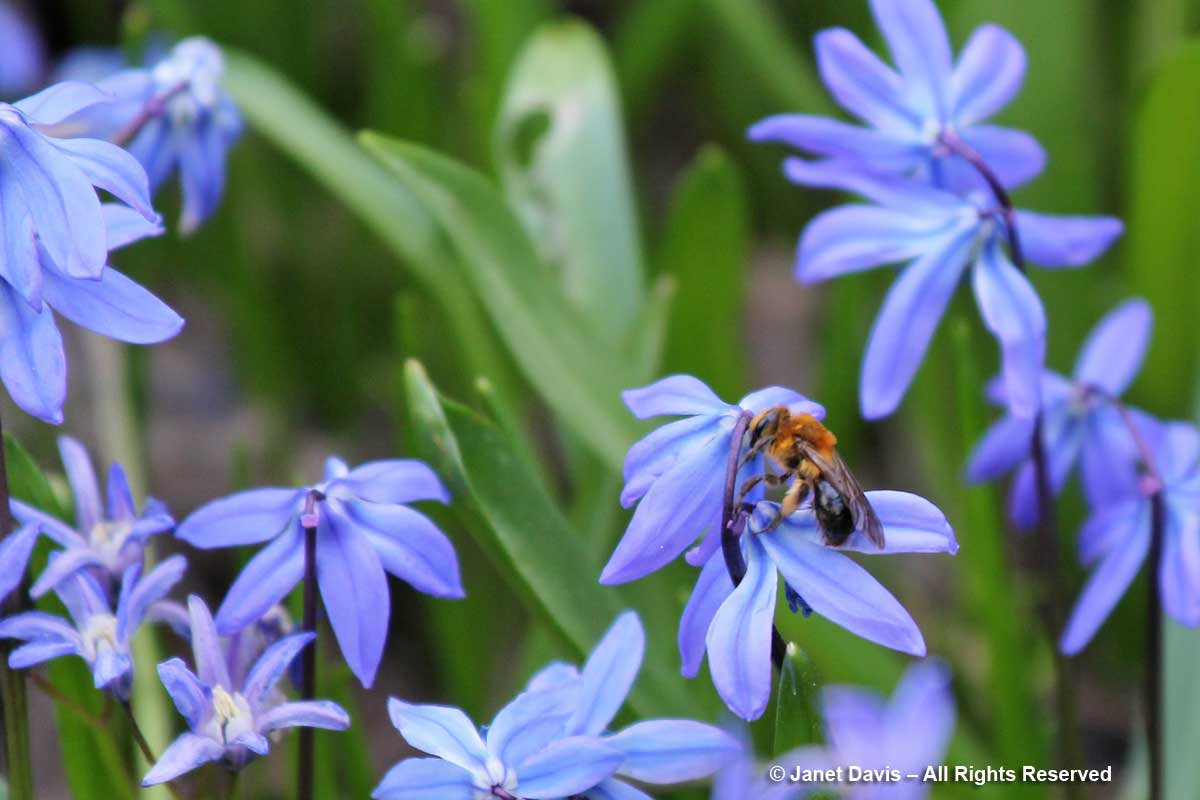
My abundant blue squill also attracts other native spring bees, including the lovely Andrena dunningi, below.
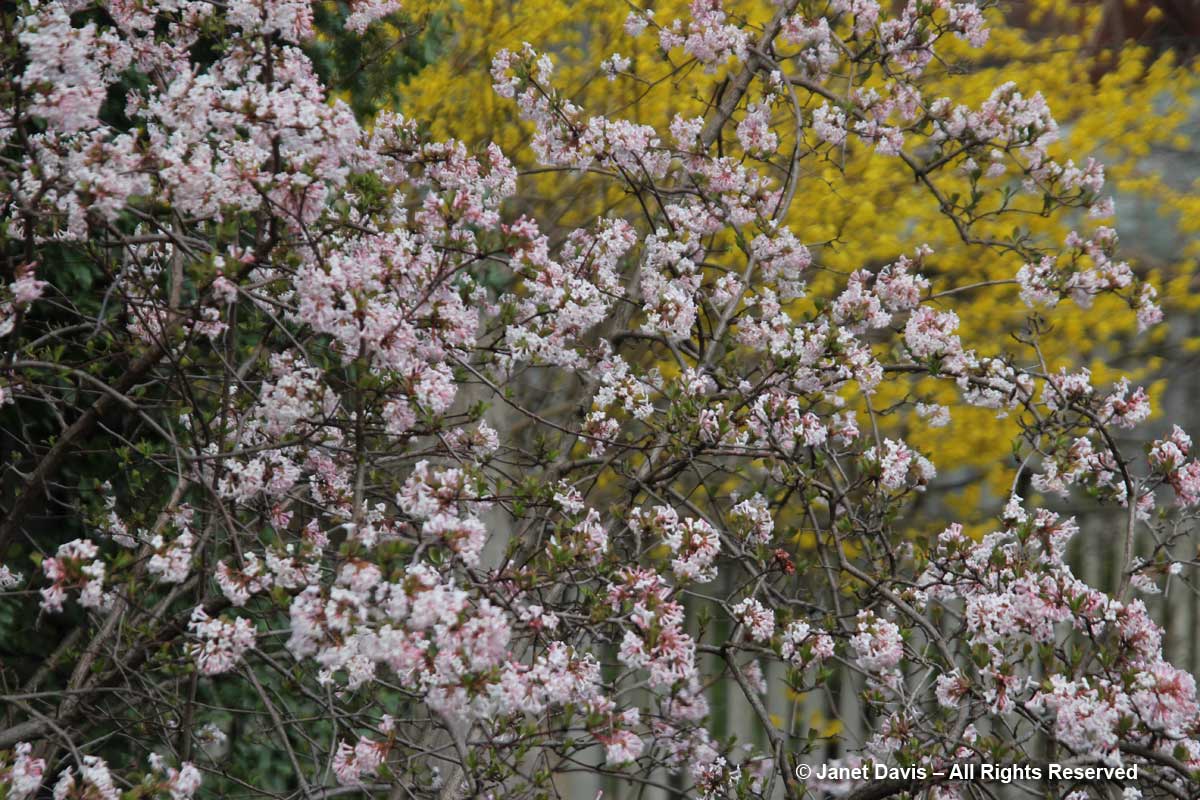
I also have a large fragrant viburnum (V. farreri) in my back garden. Native to northern China, it bursts into bloom with the first warmth of spring.
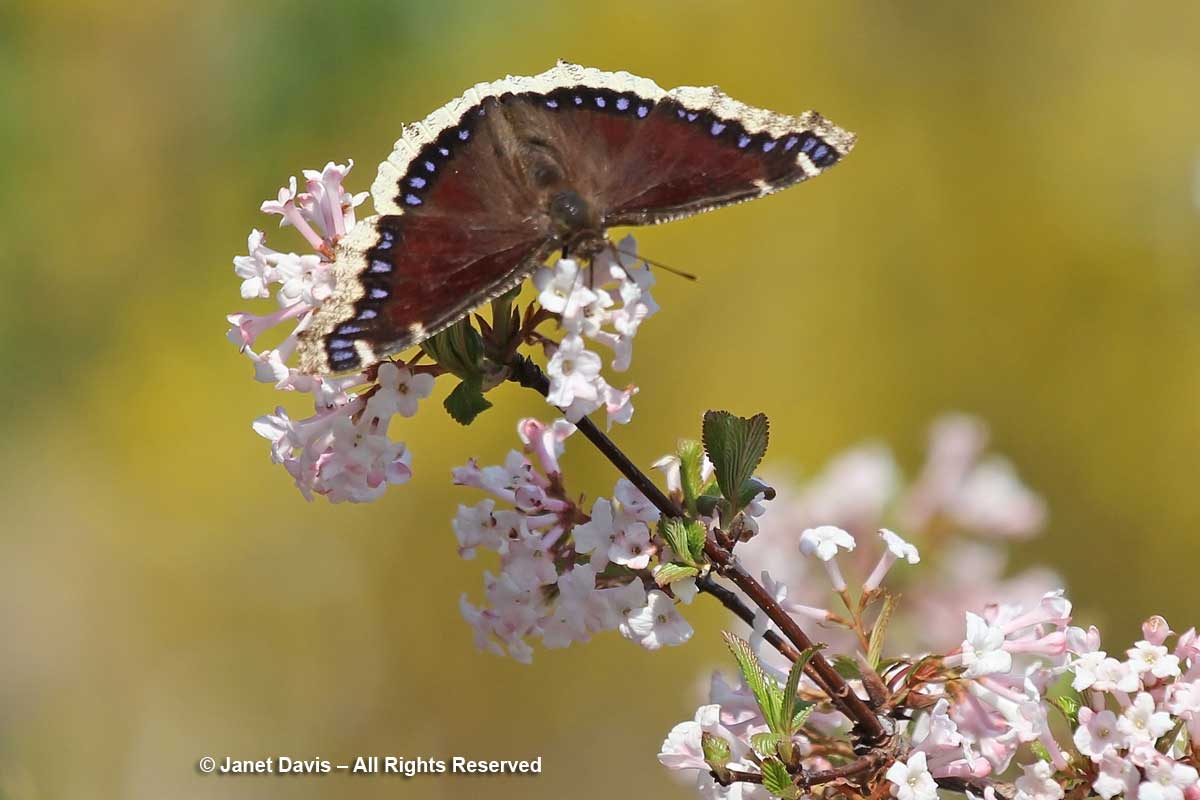
As soon as the scented flowers open, my viburnum is literally buzzing with native bees and butterflies, including mourning cloaks (Nymphalis antiopis) that have overwintered nearby…..
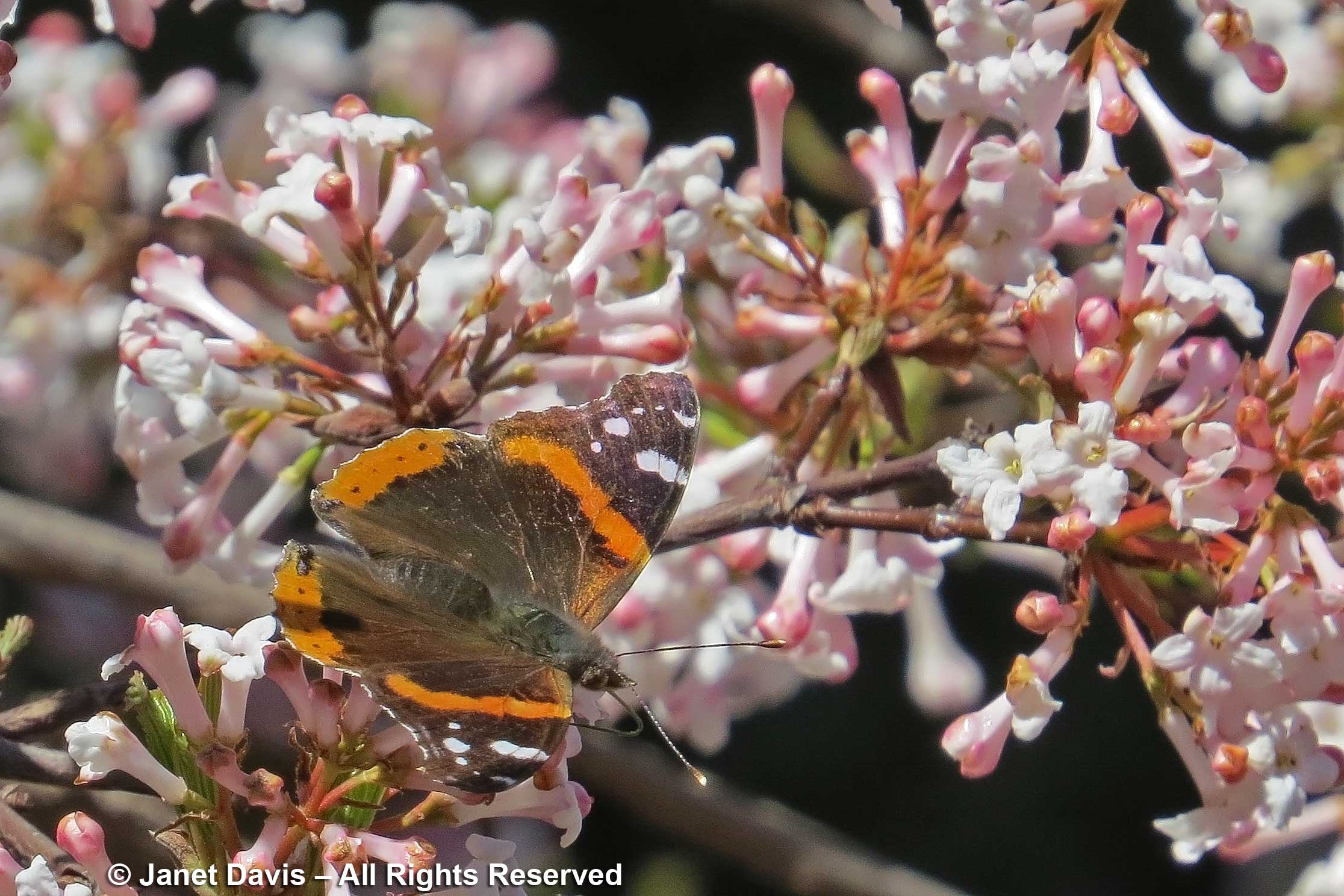
…and the odd overwintering red admiral butterfly (Vanessa atalanta).
The existential problem (not for me, but for some rigid native plant proponents) is that the alien floral nectar and pollen is making life possible for these native bees. In fact, since nobody else on my street has much in bloom at the moment and there are precious few red maples or native spring wildflowers in bloom, I am 99% sure that these bees nest in my own garden in order to attack this non-native nectar feast in early spring, as they emerge from their overwintering places.
I live in a city – in fact, the fourth largest city in North America – in which sun-loving plant species are largely all native elsewhere. As the Toronto bee brochure cited above notes: “Much of the native landscape in our region was originally forested, with the Carolinian and Mixed Forest Zones being the ecological land classifications for the area. Forests are generally not good habitats for bees, although bumble bee queens and a few early spring bees can be found foraging on the early spring flowers that are in bloom before bud burst.” My ‘native’ forest (including the maples, birches and willows on which my spring bees might have foraged) was mostly cleared, beginning more than 200 years ago, leaving a grid of streets and roads and buildings and an urban forest very much of the “planned” variety (boulevards and parks), save for our wonderful and extensive natural ravines. Though there would have been patches of meadow and bits of relict, sunny black oak savannah near High Park, most Toronto-specific native wildflowers would have been shade-lovers.
As the city’s bee brochure makes clear: “In comparison to native forests, an urban environment with patches of parkland, ravine, and large numbers of urban gardens, provides an abundance of floral and nest-site resources for bees. An evergreen forest may have no bees at all, a deciduous forest very few. But within our city there may be over 300 bee species and the average backyard garden will likely contain over 50 species, with some nesting and foraging there, and others visiting for pollen and nectar while nesting on a neighbour’s property.”
Pollination ecology is a complicated subject. Douglas Tallamy, in his excellent Bringing Nature Home: How You can Sustain Wildlife with Native Plants, writes that: “There are subtle chemical differences in nectar among plant species, but by and large, nectar from alien plants is the same as nectar from native plants.” That seems fairly clear and, extrapolating to the physical needs of Homo sapiens, carbohydrates are carbohydrates; it makes little difference whether they come from local maple syrup or granulated sugar or fructose, we will be hypoglycemic if we don’t ingest sufficient amounts. (Interestingly, “deep ecologists” separate humans from the rest of the evolved animal world – and assign us the shame of interacting in any way that benefits us above other creatures. But that’s a big and thorny subject for another day.) Tallamy goes on to say: “That said, there is growing evidence that our native bees, the andrenids, halictids, colletids, anthophorids, and megachilids, prefer native flowers to alien flowers.” He then cites the thesis findings of U of Delaware student Nicole Cerqueira, who compared visits of native bees to native and alien plants and found evidence that they showed a statistical preference for native plants in 31 instances. I’m not sure my garden is comparable, given what I’ve said about Toronto and its “native” plants, but I would be interested in seeing if quantity, i.e. massed plantings of bee-friendly alien plants, might play a spoiler role in what native bees like andrenids and colletids prefer……
In the meantime, do garden organically and do plant lots of plants for pollinators from spring to fall.